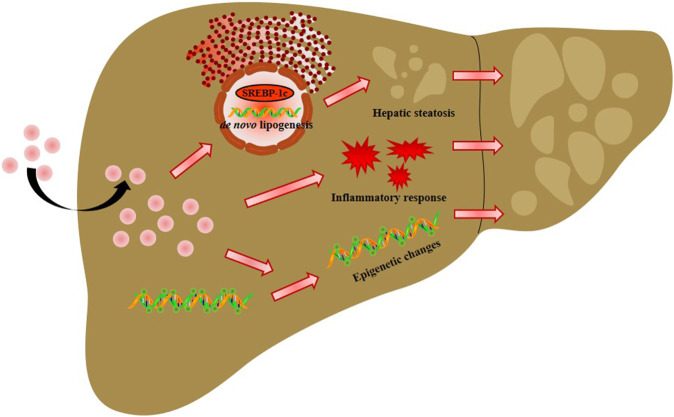
FIGURE 7.
Schema of the possible mechanisms of intravenously injected AgNPs on NAFLD development and progression. The potential mechanism of AgNP-induced hepatotoxicity in NAFLD mice is associated with hyperactivation of SREBP-1c-mediated de novo lipogenesis and liver inflammation. Additionally, significantly higher oxidative damage and lower global DNA methylation and DNA hydroxymethylation were observed in HFD-fed mice treated with AgNPs compared with NAFLD group. This study suggests that AgNP treatment exacerbated HFD-induced hepatic steatosis, liver inflammation, oxidative stress, and epigenetic changes in mice, which is relevant to the risk of AgNP exposure on NAFLD development and progression.