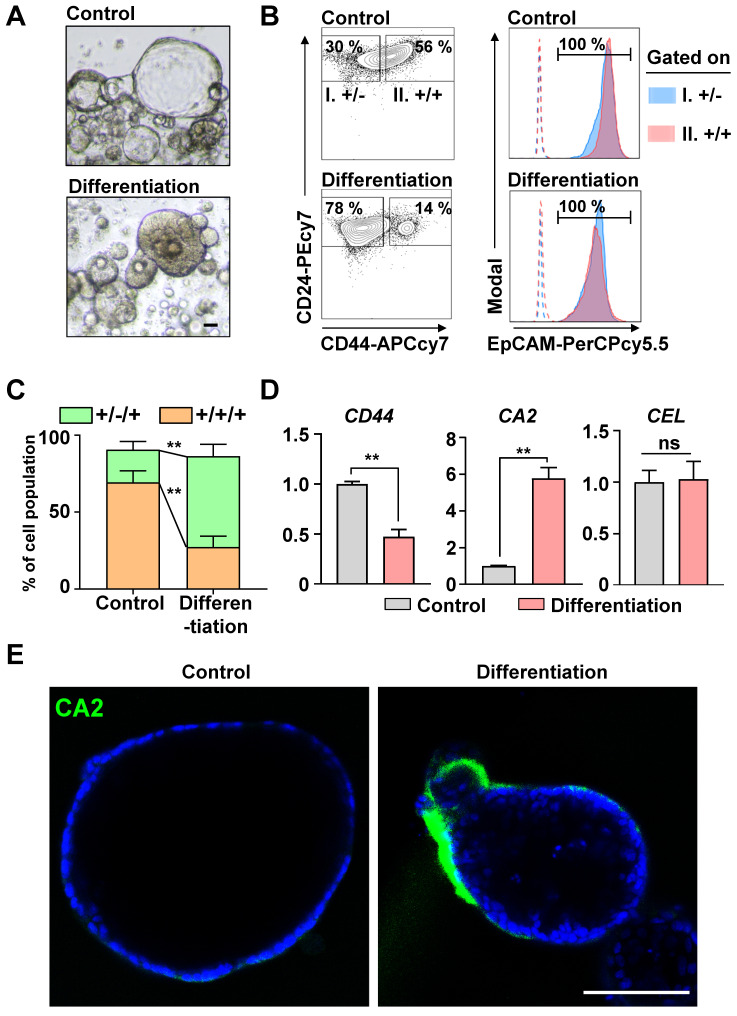
Figure 1.
Inhibiting the Wnt/NOTCH pathway caused CD44(+)CD24(+)EpCAM(+) cancer-initiating cells (CICs) to spontaneously differentiate into epithelial ductal carcinomas. (A) Representative bright-field images of control and differentiated cancer organoids. Scale bar, 40 μm. (B) Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) plot showing the surface expression of CD24, CD44, and EpCAM on human pancreatic cancer organoids and differentiated organoids. (Left) Two groups: (I) CD24(+)CD44(-) and (II) CD24(+)CD44(+) cells. (Right) EpCAM expression levels in the two groups. Dotted lines indicate fluorescence minus one (FMO). (C) Quantification of the CD24(+)CD44(-)EpCAM(+) and CD24(+)CD44(+)EpCAM(+) populations in control and differentiated organoids (N = 3 biological replicates, **P < 0.05, Sidak multiple comparisons test). (D) CD44, CA2, and CEL mRNA levels (N = 3 biological replicates with at least triplicate experiments, **P < 0.05, ns = non-significant, Mann-Whitney U test). (E) Confocal image showing CA2 (green) expression in control and differentiated cancer organoids. Scale bar, 100 µm.