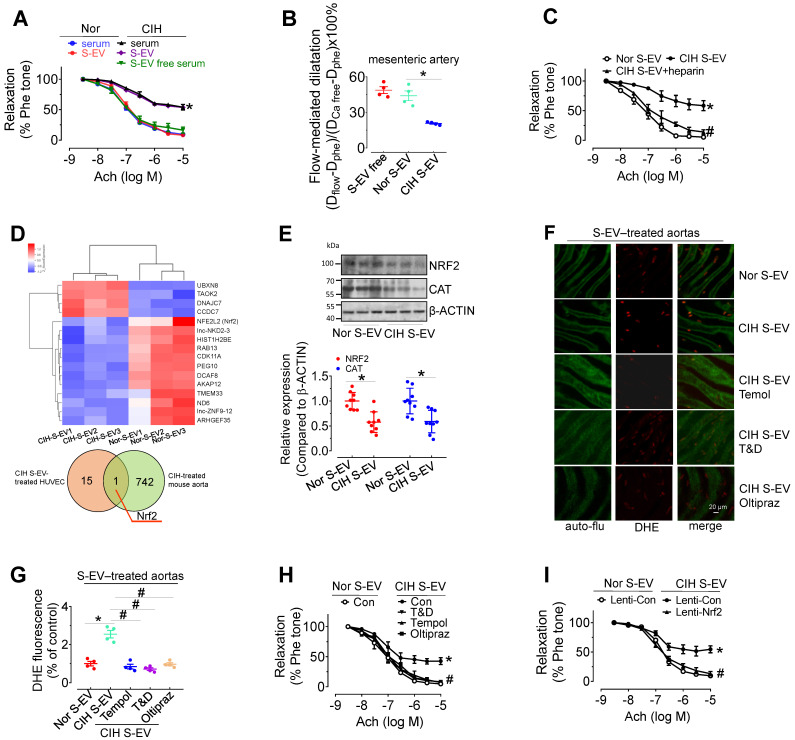
Figure 3.
CIH S-EVs impair endothelial function, augment superoxide anion production, and decrease NRF2 expression in endothelial cells. (A) 48-h treatment with serum from CIH-treated mouse attenuated EDR in mouse aortas. This effect was absent after removal of EVs from the serum, while 48-h-treatment with CIH S-EVs isolated from 1 mL of blood significantly impaired EDR in mouse aortas. (B) Exposure (48 h) to CIH S-EVs reduced flow-mediated dilatation in C57BL/6 mouse mesenteric arteries. (C) Heparin (0.3 µg/mL, 48 h) ameliorated EDR induced by CIH S-EVs. (D) Transcriptome microarray analysis was used to identify differentially expressed genes in HUVECs treated with CIH S-EVs or Nor S-EVs (up panel). The Venn diagram showed the number of overlapping genes from CIH S-EV-treated HUVECs (orange) and CIH-treated mouse aortas (green) (below panel). (E) CIH S-EV reduced the expression of NRF2 and CAT in mouse aortas. (F-G) CIH S-EV-incubation increased superoxide anion production in aortic endothelial cells detected by DHE fluorescent dye, which was blocked by 30-min pretreatment with ROS scavengers, Tempol (100 µM), or Tiron (1 mM) and DETCA (0.1 mM), or NRF2 agonist, Oltipraz (100 µM, co-culture for 48 h). Bar, 50 µm. (H) 30-min pretreatment with ROS scavengers, Tempol (100 µM), or Tiron (1 mM) and DETCA (0.1 mM), or co-culture with NRF2 agonist, Oltipraz (100 µM) for 48 h reversed CIH S-EV-induced endothelial dysfunction in aortas. (I) CIH S-EV-attenuated EDR in mouse aortas was absent after Nrf2 overexpression mediated by lentivirus. Results are the means ± SEM (n = 4-9). *P < 0.05 vs. Nor S-EV. #P < 0.05 vs. CIH S-EV. Two-way ANOVA (A, C, H, I) and two-tailed t test (B, E, G).