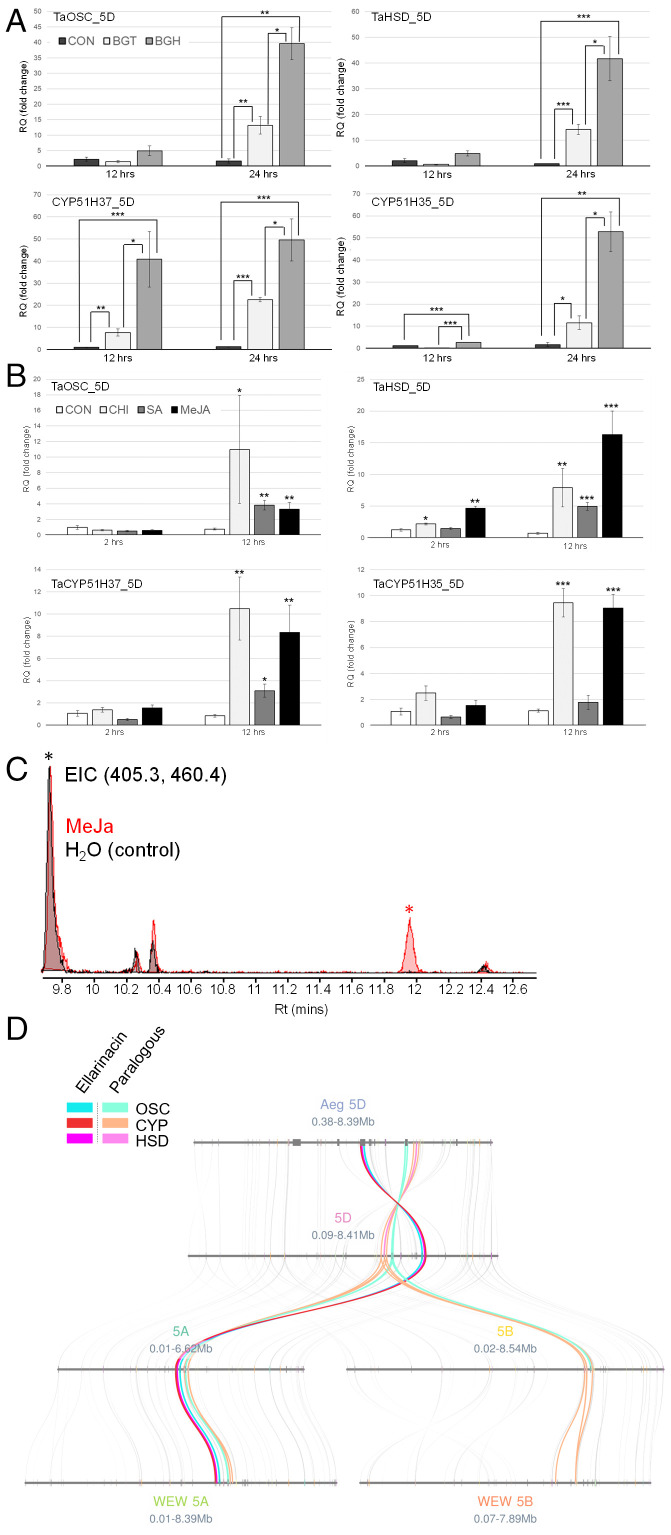
Fig. 4.
Ellarinacin BGC 3(5D) is induced by pathogens and elicitors. (A) Quantitative real-time PCR of ellarinacin BGC genes in detached wheat leaves infected with two powdery mildew isolates, 12 and 24 h post infection. BGT and BGH, infected with wheat-adapted isolate B. graminis f. sp. tritici or the nonadapted isolate B. graminis f. sp. Hordei, respectively; CON, control (noninfected). (B) Quantitative real-time PCR for ellarinacin BGC genes in detached wheat leaves treated with MeJa, SA, chitin (CHI), or H2O (CON), for 2 or 12 h. For A and B, relative quantification values (in fold change) indicate means of three biological replicates ± SEM. Asterisks denote t test statistical significance of differential expression. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (C) GC-MS analysis of TMS-derivatized extracts from wheat leaves treated with MeJa or H2O (control) for 3 d. EICs are for ions representing ellarinacin (405.3, Rt 11.94, red asterisk) and 5α-cholestan-3β-ol (460.4, Rt 9.70, black asterisk). (D) Microsynteny analysis of the region surrounding the ellarinacin BGC and its paralogous cluster on Chr.5 of the wheat A, B, and D genomes, and wheat progenitors A. tauschii (Aeg) and wild emmer wheat (WEW).