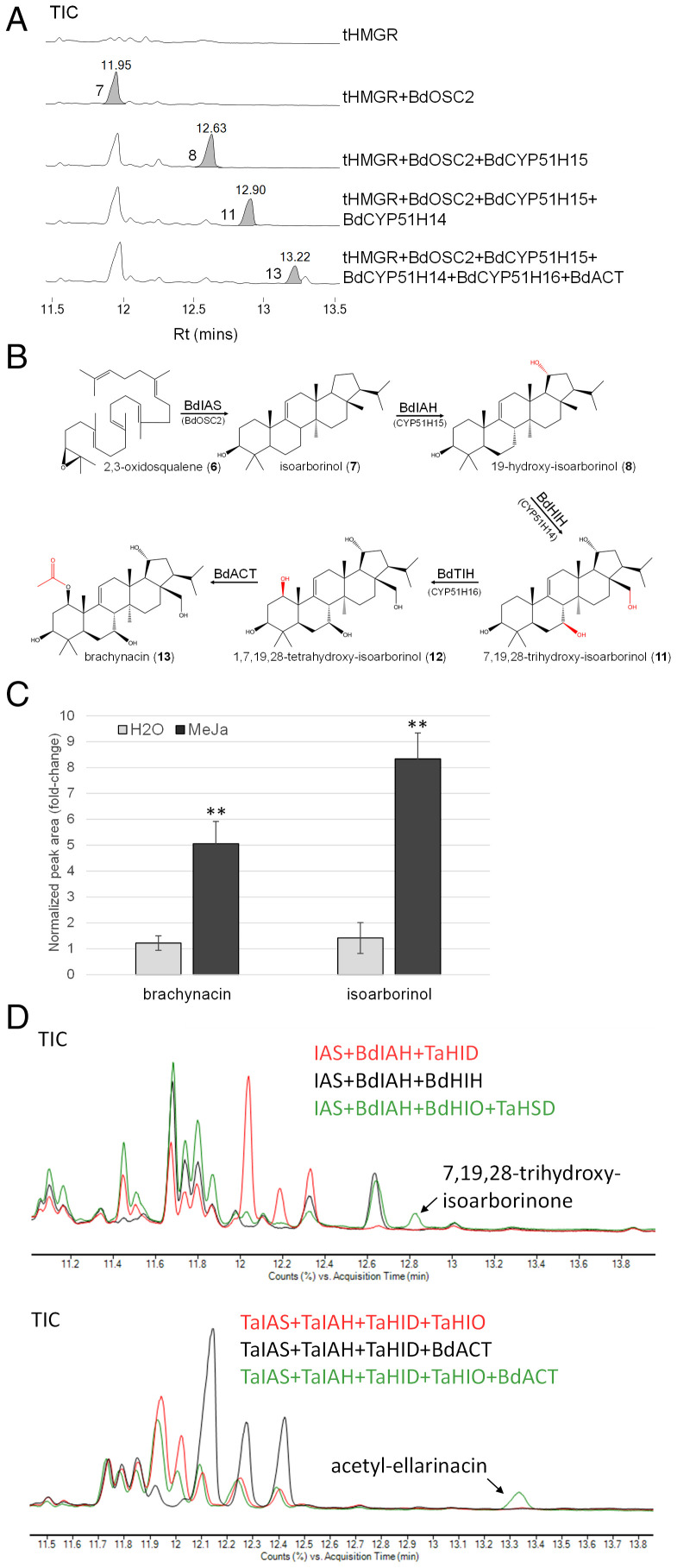
Fig. 6.
B. distachyon BGC produces the isoarborinol-derived triterpenoid, brachynacin. (A) GC-MS traces for B. distachyon cluster genes transiently expressed in N. benthamiana. Marked peaks were identified as isoarborinol (7), 19-hydroxy-isoarborinol (8), 7,19,28-trihydroxy-isoarborinol (11), and brachynacin (13) (494.5). (B) Assigned structures and predicted biosynthetic pathway of brachynacin in B. distachyon. BdACT, 1,7,19,28-tetrahydroxy-isoarborinol acetyltransferase; BdIAH, isoarborinol hydroxylase; BdIAS, isoarborinol synthase; BdHIH, 19-hydroxy-isoarborinol hydroxylase; BdTIH, 7,19,28-trihydroxy-isoarborinol hydroxylase. (C) Relative abundance of isoarborinol and brachynacin in TMS-derivatized extracts of B. distachyon leaves treated with MeJa or H2O for 12 h. Relative quantification is based on normalized peak areas in GC-MS analysis of four biological replicates. Means of four biological replicates ± SEM are shown. Asterisks denote t test statistical significance. **P < 0.01. (D) GC-MS TICs of N. benthamiana leaves transiently expressing combinations of wheat and B. distachyon genes.