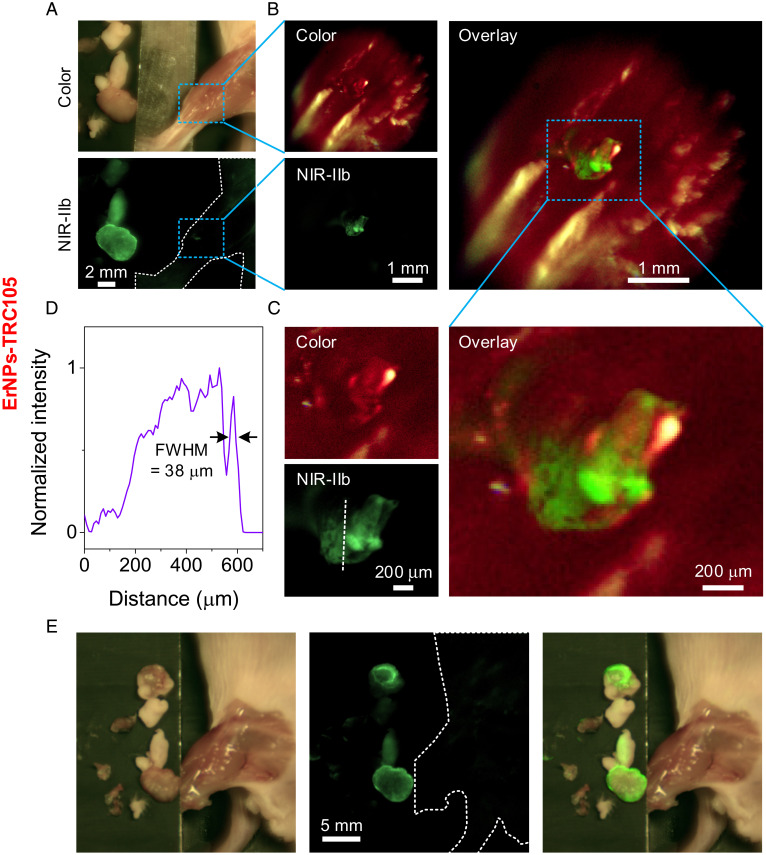
Fig. 5.
Residual tumor fragments’ precise removal navigated by our portable imager with high magnification and resolution. (A) Color and NIR-IIb imaging of the surgery area after tumor removal observed by the highest magnification of the zoomable lens set with a FOV of 22 × 18 mm2. When the 4T1 tumor size reached ∼4 to 8 mm (typically 3 to 6 d after inoculation), ErNPs-TRC105 was injected i.v. The surgery was performed 24 h p.i. (B) High-magnification imaging resolved a small residual tumor fragment after main tumor removal, performed by replacing the front lens of zoomable lens with a 5× objective (NA = 0.12, FOV: 5.8 × 4.7 mm2). (C) High-magnification imaging of the rectangular highlighted region in B. (D) A normalized intensity profile along the dotted line in C revealing structures with a feature size of 38 μm. (E) Low-magnification imaging of surgery area using zoomable lens set with a FOV of 44 × 34 mm2 after tumor removal under high-resolution view.