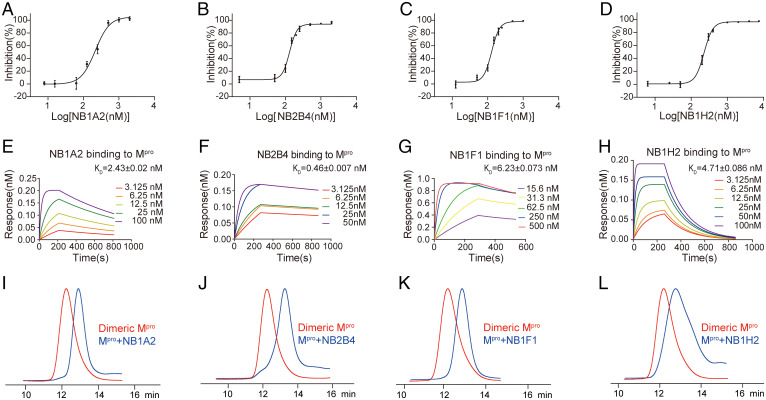
Fig. 1.
Generation and characterization of camelid inhibitory nanobodies against SARS-CoV-2 Mpro. (A–D) The hydrolytic activity of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro was measured in the presence of increasing concentrations of the inhibitory nanobodies NB1A2 (A), NB2B4 (B), NB1F1 (C), and NB1H2 (D). (E–H) Biolayer interferometry binding kinetics measurements for NB1A2 (E), NB2B4 (F), NB1F1 (G), and NB1H2 (H) (KD, equilibrium dissociation constant). (I–L) Representation of SEC profiling of the dimeric Mpro (red) and dimeric Mpro + NB complex (blue); dimeric Mpro + NB1A2 complex (I), dimeric Mpro + NB2B4 complex (J), dimeric Mpro + NB1F1 complex (K), and dimeric Mpro + NB1H2 complex (L).