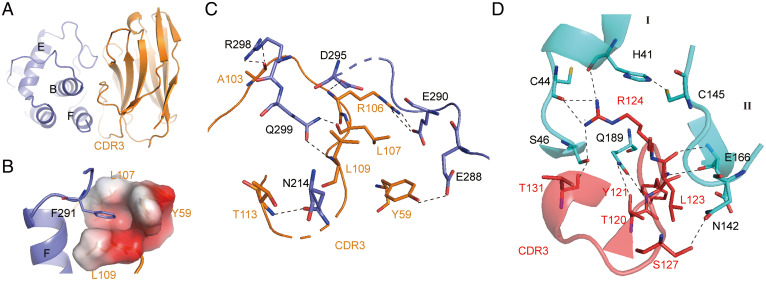
Fig. 3.
Structural mechanism of inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro by NB2B4 and NB1A2. (A) The epitope of NB2B4 on the C-terminal domain of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro, with the C-terminal domain colored in blue and NB2B4 colored in orange, respectively. (B) The residues F291 of the F helix from the C-terminal domain are inserted into the hydrophobic pocket composed of residues Y59, L107, and L09 of NB2B4. Residue F291 is shown as a stick model; residues Y59, L107, and L09 of NB2B4 are shown as the electrostatic surface to illustrate the hydrophobic pocket. (C) Close-up views of the interface between SARS-CoV-2 extended Mpro (blue) and NB2B4 (orange). (D) Close-up views of the interface between SARS-CoV-2 compact Mpro (cyan) and NB1A2 (purple). The key residues involved in interaction are shown as stick models. Polar interactions are indicated with black dashed lines.