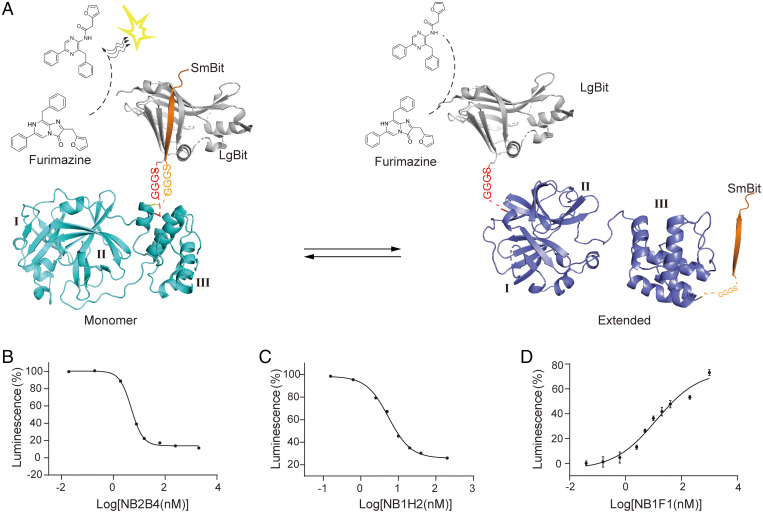
Fig. 5.
Establishing a NanoBit-based conformational sensor for the monomeric SARS-CoV-2 Mpro. (A) Schematic of NanoBiT complementation to examine conformation changes in monomeric Mpro. Crystal structures of the compact state colored in cyan (Left) and the extended conformation colored in blue (Right). The Mpro was fused at its N terminus with LgBiT (gray) and at C terminus with SmBiT (yellow). The GGGS linker was inserted between N terminus/C terminus and LgBiT/SmBiT. The N-terminal LgBiT was expected to bind in close proximity to the C-terminal SmBiT in the compact conformation of Mpro, and increase the possibility of LgBiT-SmBiT complementation and the complemented luminescence, while it decreases in the extended conformation. (B–D) Luminescence signal measured for NB2B4 (B), NB1H2 (C), and NB1F1(D) in different concentrations; the pIC50 values for NB2B4 and NB1H2 are 4.94 nM and 5.48 nM, respectively; the pEC50 of NB1F1 is 12.61 nM. Data are mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments performed in triplicates and normalized to the maximum response of the control.