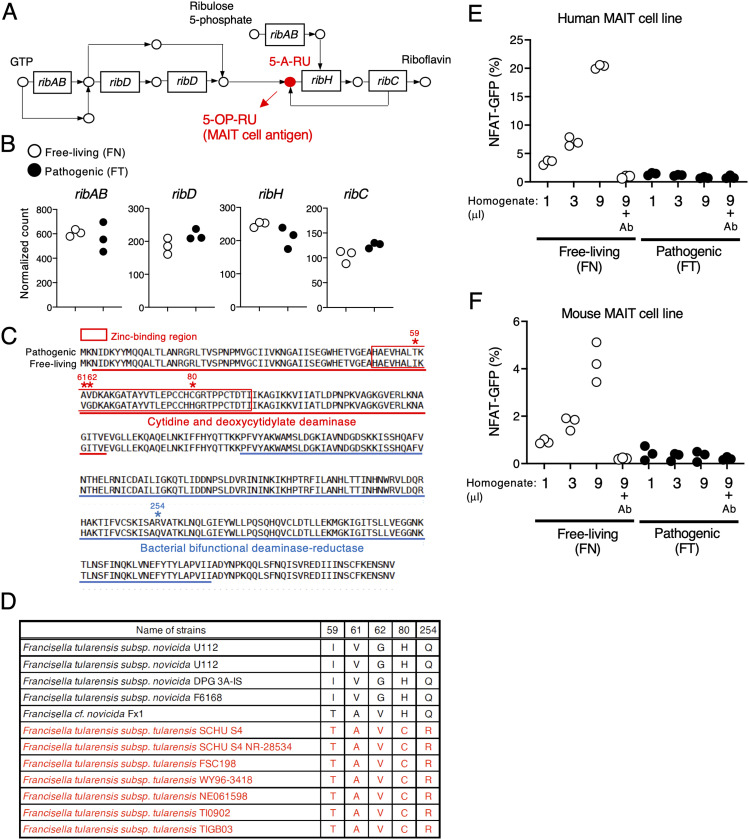
Figure 2. FT has mutations in ribD and does not activate MAIT cells.
(A) Schematic of the riboflavin synthetic pathway. The precursor of the MAIT cell antigen presented by MR1 is highlighted in red. (B) Plots of normalized read counts of genes ribAB, ribD, ribH, and ribC in the free-living and pathogenic strains. (C) Comparison of the amino acid sequence of RibD in the pathogenic and free-living strain. Boxed amino acids (red) are the zinc-binding region of the cytidine and deoxycytidylate deaminase domain. Underlined amino acid sequences are catalytic domains. (D) Summary table of amino acids at five defined positions in RibD in free-living (black) and pathogenic (red) strains as found in the KEGG database. (E, F) GFP-reporter activities of cells expressing human (E) and mouse (F) MAIT TCRs after stimulation with escalating amounts (1, 3, 9 μl) of total metabolites from the indicated strains that were cultured in the presence of human and mouse MR1-expressing cells, with or without anti-MR1 antibody (Ab) (10 μg/ml). Data are representative of three independent experiments.