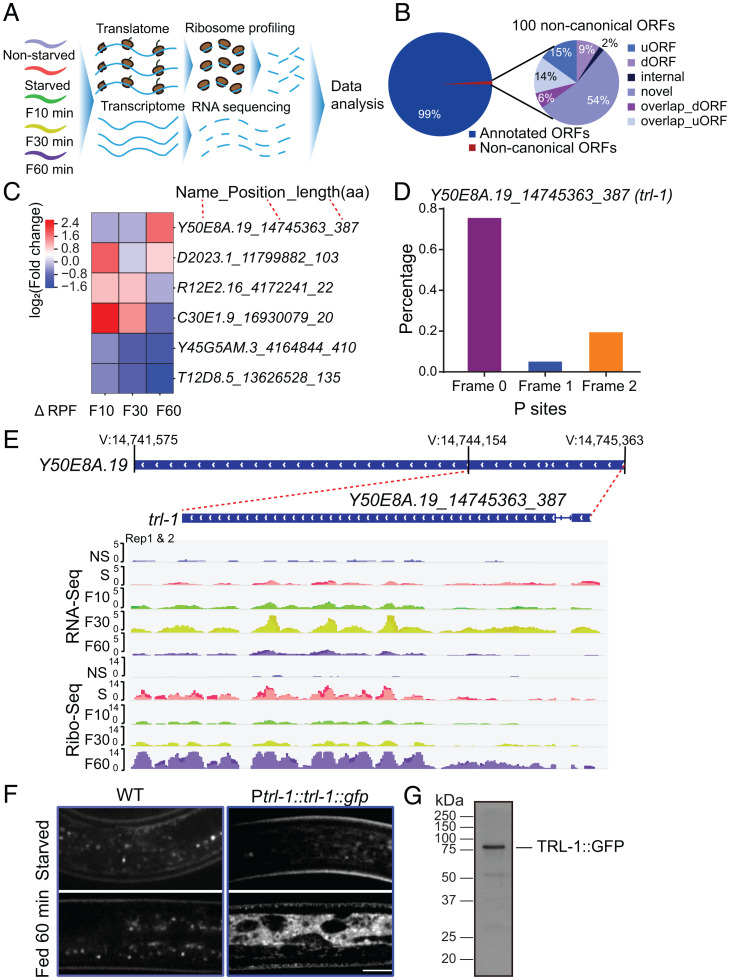
Fig. 1.
trl-1 translates upon refeeding. (A) Schematic overview of the experimental procedure. (B) Pie chart of the percentage breakdown of protein-coding genes annotated from Ribo-Seq by RiboCode (CPM ≥ 1). The noncanonical ORFs are classified into uORF, dORF, internal ORF, novel ORF, overlap_dORF, and overlap_uORF. (C) Heatmap of the top differentially regulated novel ORFs [log2(fold change), adjusted P ≤ 0.05] associated with ribosomes after refeeding stimulation in C. elegans. (D) RiboCode analysis of ribosome P sites distribution in the expected reading frame for noncanonical ORF Y50E8A.19_14745363_387(trl-1). (E) Patterns of RNA-Seq transcriptional reads (Top) and ribosome profiling translational reads (Bottom) for trl-1 from nonstarved (NS), starved (S), refed 10-min (F10), 30-min (F30), and 60-min (F60) worms. The trl-1 gene structure is in the center, with a thin blue line representing the intron and wide blue rectangles indicating exons. (F) Representative imaging of WT (N2) and TRL-1::GFP dauer under starvation or refed 60-min conditions. TRL-1::GFP stands for the GFP fusion to the C-terminal of TRL-1. (Scale bar, 5 μm.) (G) Western blot analysis of the TRL-1::GFP protein in C. elegans.