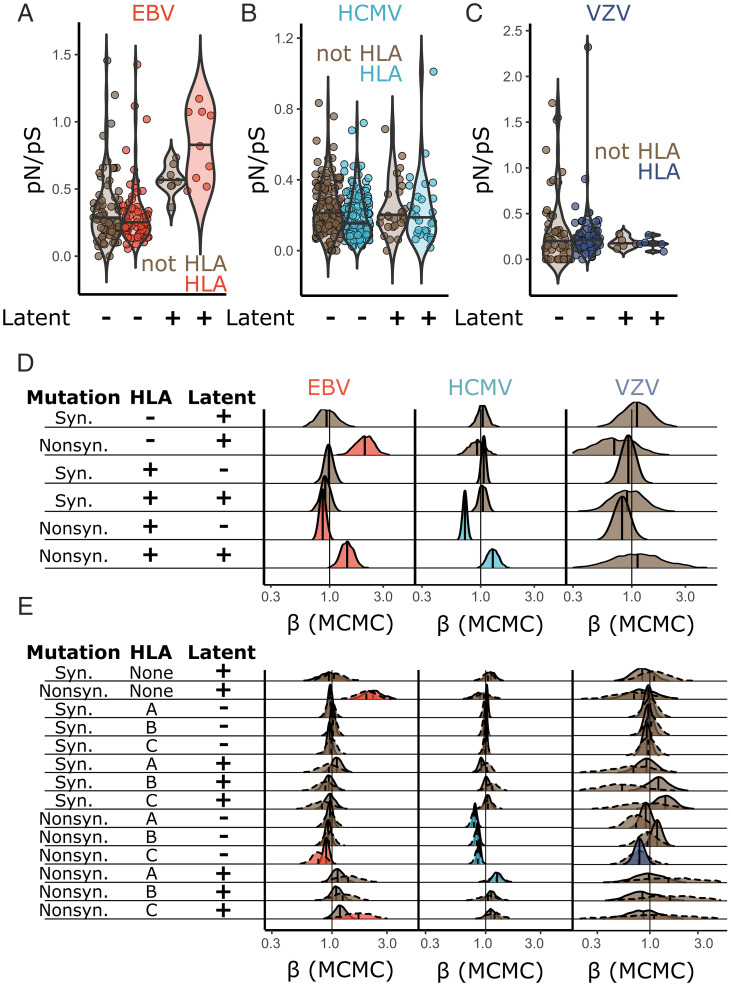
Fig. 2.
HLA recognition of latency genes is associated with higher levels of amino acid polymorphism. (A–C) pN/pS was calculated in HLA binding and nonbinding regions of each herpesvirus protein. Analogous data for regions recognized by HLA-A, HLA-B, and HLA-C are presented in SI Appendix, Fig. S4. The significance between observed pN/pS values (A–C) was assessed using a Bayesian SnIPRE-like Poisson mixed model in Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC)glmm (SI Appendix, Eq. 1); the output is summarized in D. Each distribution in D is the posterior distribution of the model coefficients (β), where a value of less than one indicates a smaller polymorphism count associated with the corresponding class of mutation. A value of greater than one indicates a greater count associated with the corresponding class. Colored distributions reflect significance at P < 0.05. E presents the same model as D but with regions of each viral protein split into HLA-A, HLA-B, or HLA-C. Solid lines indicate that the data modeled used all peptides recognized by a particular HLA protein (A, B, or C); dotted lines show a model using only peptides recognized uniquely by a single HLA protein (A, B, or C).