(
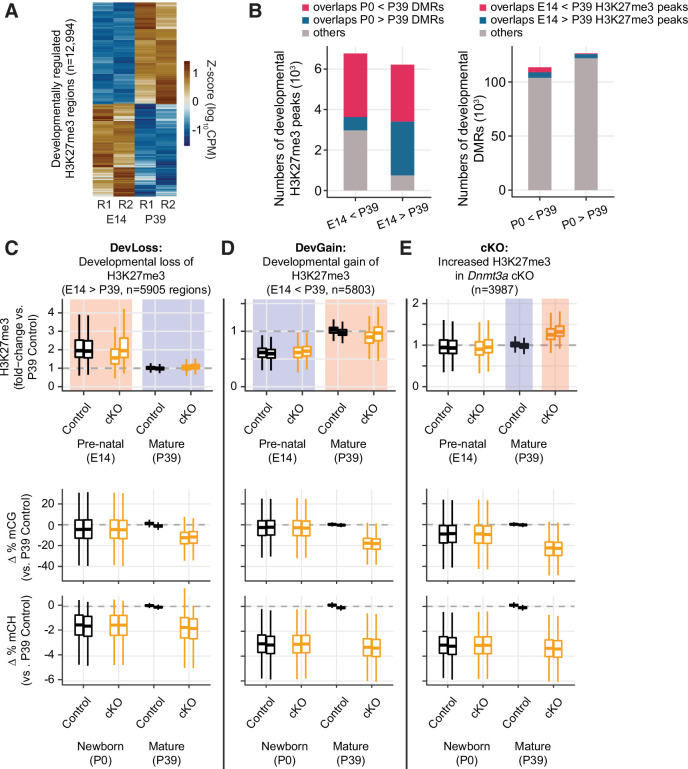
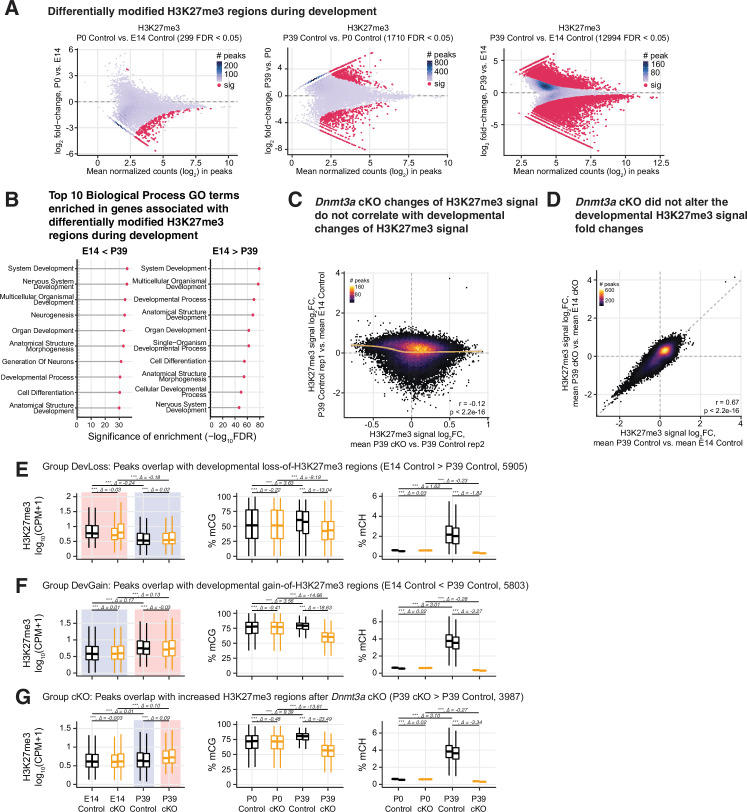
A) Differentially modified H3K27me3 regions during development in control samples. (
B) Top 10 most enriched biological process terms from the Gene Ontology in the genes associated with differentially modified H3K27me3 regions during development in control samples. Gene-region association was predicted by GREAT (
McLean et al., 2010). FDR, false discovery rate; the vertical dashed line shows the threshold of FDR = 0.05. (
C) Correlations of P39 H3K27me3 signal fold-changes of
Dnmt3a cKO vs. control and developmental H3K27me3 signal fold-changes of P39 vs. E14 in H3K27me3 chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq) peaks. Note that peaks with big absolute fold-changes in P39 cKO vs. P39 control are generally not changed much in P39 control vs. E14 control, and vice versa. Replicates 1 and 2 of P39 control are used in the y and x axis, respectively, to avoid double-dipping. The smoothed line is fitted using a generalized additive model, and the shaded area shows the 95% confidence interval of the fit. r, Spearman correlation coefficient. (
D) The developmental H3K27me3 signal fold-changes are not affected by
Dnmt3a cKO. r, Spearman correlation coefficient. (
E–G) Boxplots to show the distribution of H3K27me3 signal, mCG, and mCH levels in peaks that overlaps with E14 vs. P39 developmental loss-of-H3K27me3 regions (
E), peaks that overlap with developmental gain-of-H3K27me3 regions (
F), and peaks that overlap with increased H3K27me3 regions in P39
Dnmt3a cKO (
G). Asterisks show the significances from paired t-tests (***, p<0.001). ∆ values are the mean of the differences for the two groups in comparison (group on the right vs. group on the left).