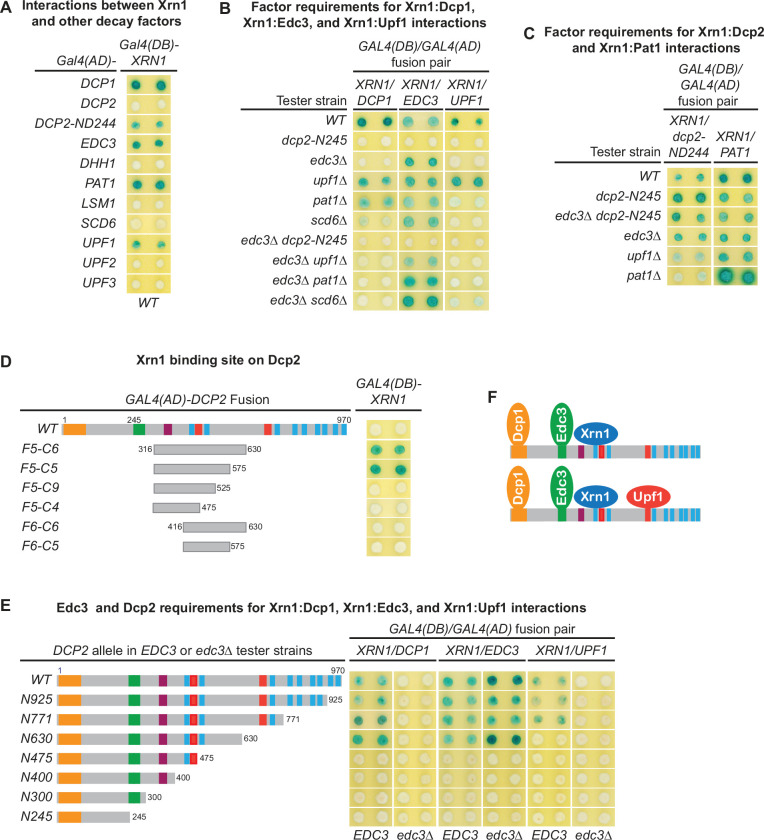
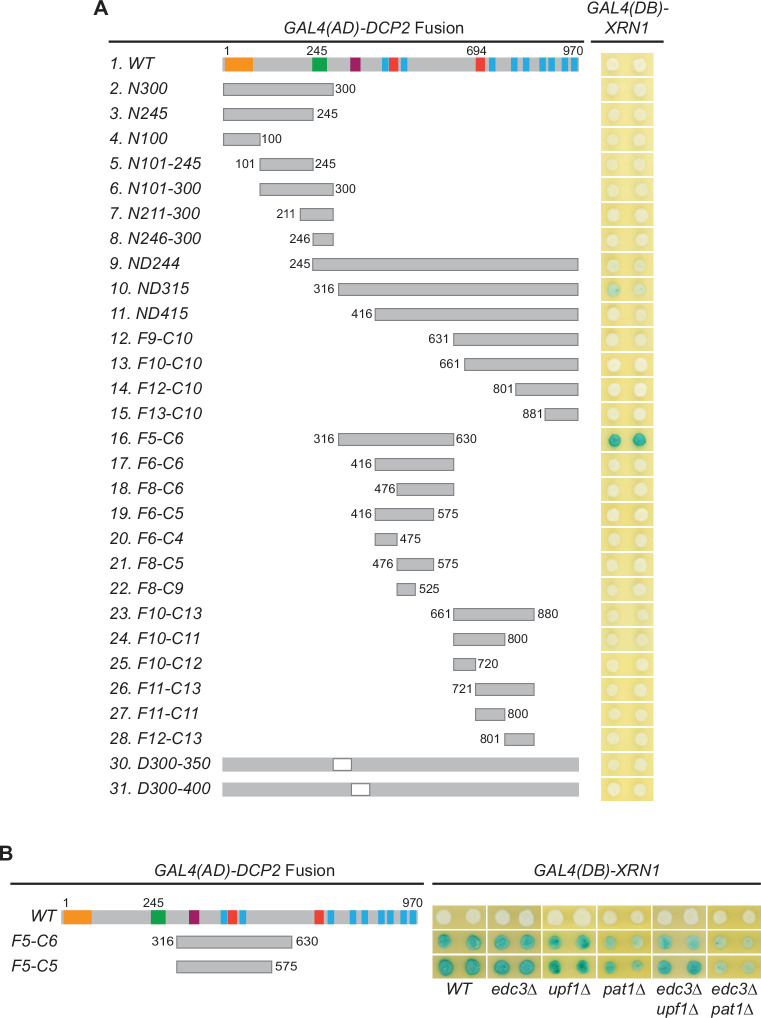
Figure 6. Xrn1 binds to Dcp2 and is directly recruited to different decapping complexes by Dcp2.
(A) Two-hybrid analyses of Xrn1 interactions with Dcp1, Edc3, Pat1, Upf1, and an N-terminally truncated Dcp2 fragment in WT cells. (B) Two-hybrid analyses of Dcp2-bridged interactions between Xrn1 and Dcp1, Edc3, or Upf1. (C) Two-hybrid analyses of interactions between Xrn1 and Pat1 or N-terminally truncated Dcp2. (D) Two-hybrid analyses of Xrn1 binding to an internal Dcp2 fragment. See also Figure 6—figure supplement 1. (E) Dcp1:Xrn1, Edc3:Xrn1, and Upf1:Xrn1 interactions in tester strains harboring Dcp2 C-terminal truncations and EDC3 or edc3Δ alleles. (F) Two different Xrn1-containing decapping complexes inferred from two-hybrid analyses in B and E. Allele schematics and two-hybrid analyses as in Figure 1.