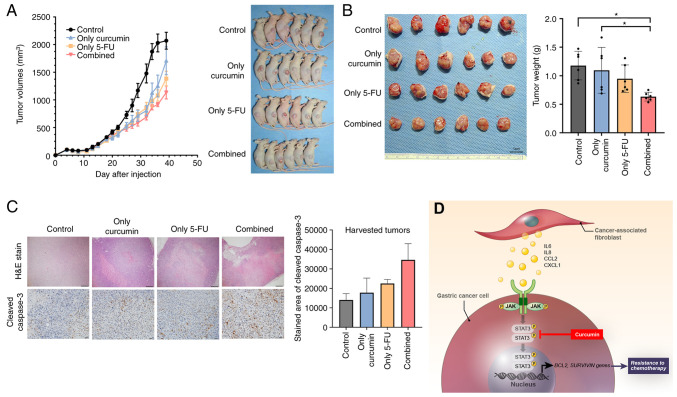
Figure 5.
GC xenograft tumor growth inhibition by combination treatment with Curcumin and 5-FU. (A) Mice growing subcutaneous tumors were randomized to receive 21 intraperitoneal injections three times a week of either DMSO or 5-FU or curcumin or combined treatment (5-FU + curcumin). The tumor volume was measured using calipers (n=6 mice in each group) (B) The tumor weight was measured using a precision electronic balance. Representative images of excised tumors in SNU668 models. Scale bar, 1 cm. (C) Representative micrographs showing H&E staining and immunohistochemical staining for cleaved caspase-3 in harvested xenograft tumors derived from SNU668 cells mixed with CAFs after treatment. Scale bar, 100 µm. (D) Schematic diagram of the findings of the present study. CAF-induced cytokines activate the JAK2/STAT3 pathway in gastric cancer cells via paracrine signaling, which allows tumor cells to increasingly oppose apoptosis and increase their survival and resistance to chemotherapy. Curcumin, inhibitor for STAT3, that is a nature product, inhibits the CAF-induced activation of the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in GC cells and consequently enhance the efficacy of chemotherapeutic drugs. 5-FU, 5-fluorouracil; GC, gastric cancer; CCL2, C-C motif chemokine ligand 2; CAF, cancer-associated fibroblast; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; IL-6, interleukin-6; IL-8, interleukin-8; JAK, Janus-activated kinase; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. *P<0.05.