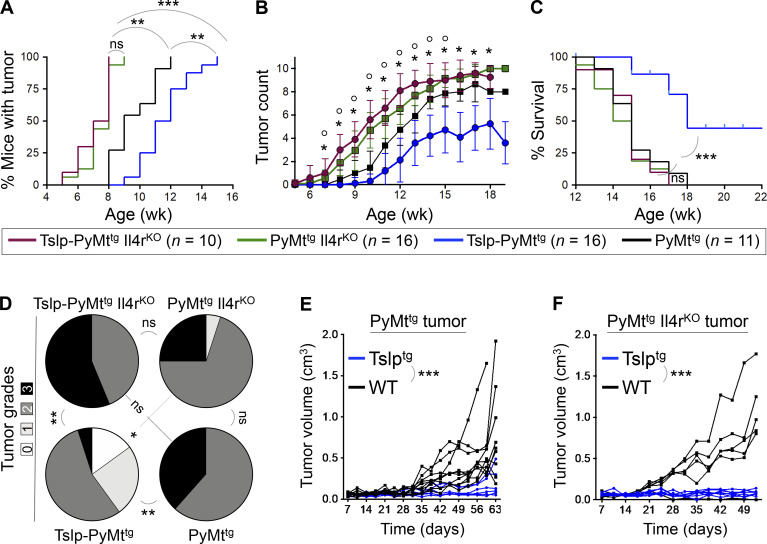
Figure 4.
Th2 cell polarization mediates the immunity against breast carcinogenesis. (A–C) Comparison of tumor outcomes across Tslp-PyMttg Il4rKO, PyMttg Il4rKO, Tslp-PyMttg, and PyMttg mice including time to tumor onset (log-rank test; A), number of tumors per mouse over time (*, P < 0.005 comparing Tslp-PyMttg Il4rKO to Tslp-PyMttg and °, P < 0.05 comparing PyMttg Il4rKO to PyMttg, Mann–Whitney U test; B), and percentage survival of the animals in the four groups (log-rank test; C). (D) Distribution of histological grades of Tslp-PyMttg Il4rKO (n = 16), PyMttg Il4rKO (n = 20), Tslp-PyMttg (n = 20), and PyMttg (n = 13) tumors (Fisher’s exact test). (E) Tumor growth kinetic in Tslptg (test, n = 6, 6/6 tumors were <0.5 cm3 at the endpoint) versus WT (control, n = 10, 3/10 tumors were <0.5 cm3 at the endpoint) mice implanted with PyMttg primary breast tumors (two-way ANOVA). (F) Tumor growth kinetics in Tslptg (test, n = 7, 7/7 tumors were <0.5 cm3 at the endpoint) and WT (control, n = 5, 0/5 tumors were <0.5 cm3 at the endpoint) mice implanted with PyMttg Il4rKO primary breast tumors (two-way ANOVA). Each of the tumors in the studies is from a separate mouse. All experimental data verified in at least two independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.0001.