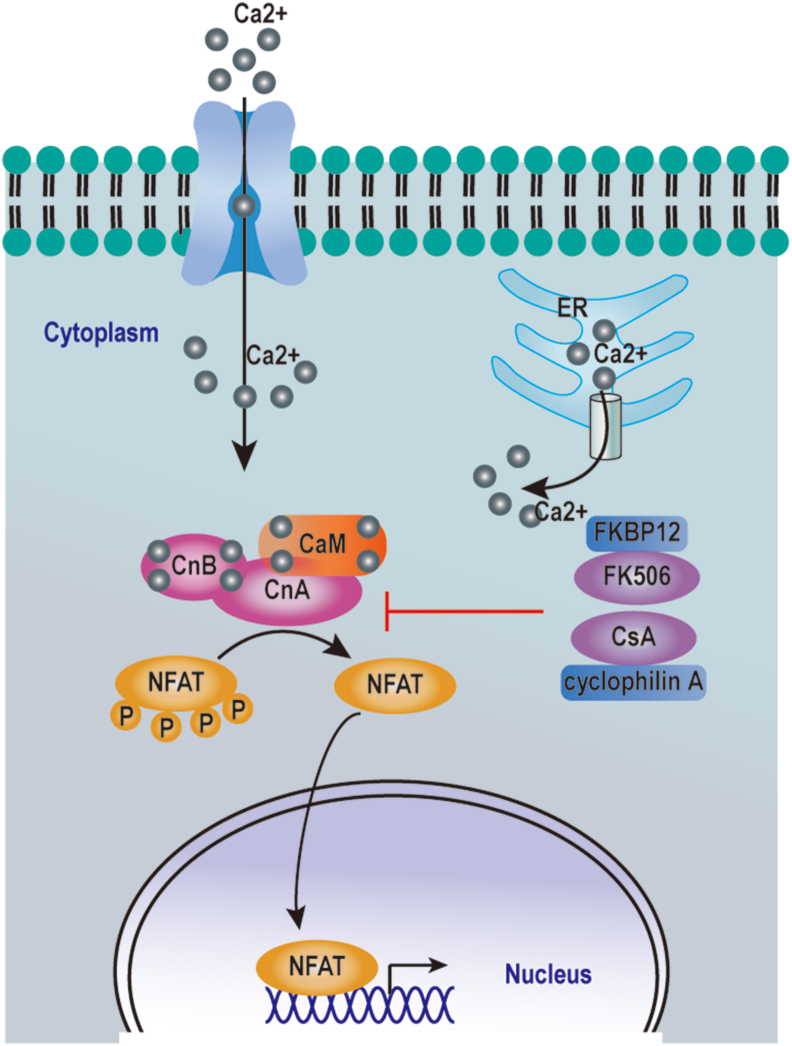
Figure 2.
The CaN-NFAT pathway in T cells. Intracellular and extracellular signals trigger an initial cytoplasmic Ca2+ increase. Elevated cytoplasmic Ca2+ activates CaN, which dephosphorylates the NFAT transcription factors, causing NFATs to translocate into the nucleus and initiate gene transcription. CsA and FK506 inhibit the activity of CaN through their interaction with the immunophilins called cyclophilin A and FK-binding protein 12 (FKBP12) respectively.