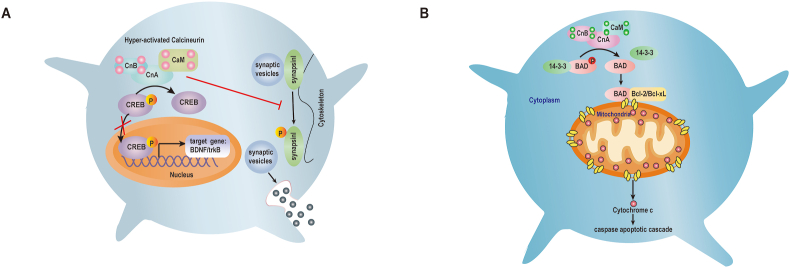
Figure 4.
Role of activated CaN in synaptic dysfunction and neuronal death. (A) (1) Activated CaN dephosphorylates CREB, inhibiting its translocation to the nucleus and reducing CREB target gene expression required for neuronal growth and synaptic plasticity. (2) Activated CaN dephosphorylates synapsin I, inhibiting neurotransmitter release by abrogating synaptic vesicle transport. (B) CaN dephosphorylates BAD, which dissociates from scaffolding proteins and forms a dimer with Bcl-2 or Bcl-xL, leading to the release of cytochrome c and the apoptotic cascade that results in neuronal cell death.