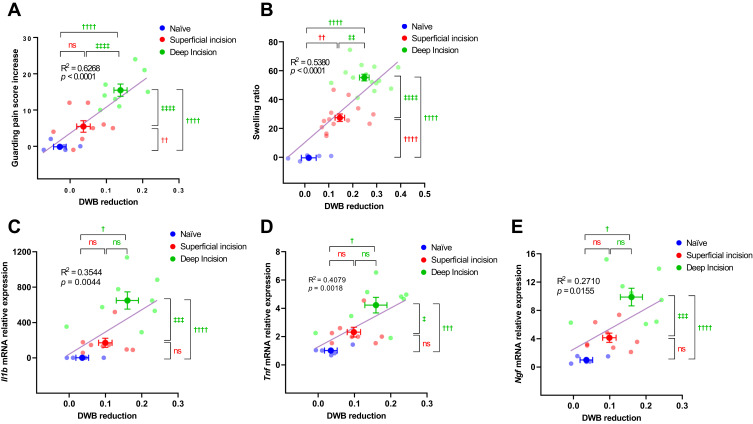
Figure 3.
Evaluations of inflammatory responses and pain-like behaviors in different incisional pain models.
Notes: Changes were evaluated at baseline and 6 h post-surgery in the superficial incisional pain model (n = 8) and deep incisional pain model (n = 8) compared with naïve animals (n = 5). (A) Correlation between the increase in the cumulative guarding pain score and reduction in weight distribution in the ipsilateral paw at 6 h post-surgery. (B) Correlation between the swelling ratio (increased ipsilateral hind paw thickness to baseline ratio) and reduction in weight distribution on ipsilateral paw at 6 h after surgery. (C–E) Correlation between the fold changes in mRNA expression of inflammatory factors Il1b (C), Tnf (D) and Ngf (E) in ipsilateral hind paw skins and the reduction in weight distribution on ipsilateral paw at 6 h after surgery. Data were expressed as mean ± SEM, assessed by two-way ANOVA with repeated measures followed by Šídák’s multiple comparisons test. †p < 0.05; ††p < 0.01, †††p < 0.001, ††††p < 0.0001 vs naïve; ‡p < 0.05, ‡‡p < 0.01, ‡‡‡p < 0.001, ‡‡‡‡p < 0.0001 deep incision vs superficial incision.
Abbreviations: BL, baseline; POD, postoperative day; R2, Pearson’s correlation coefficient.