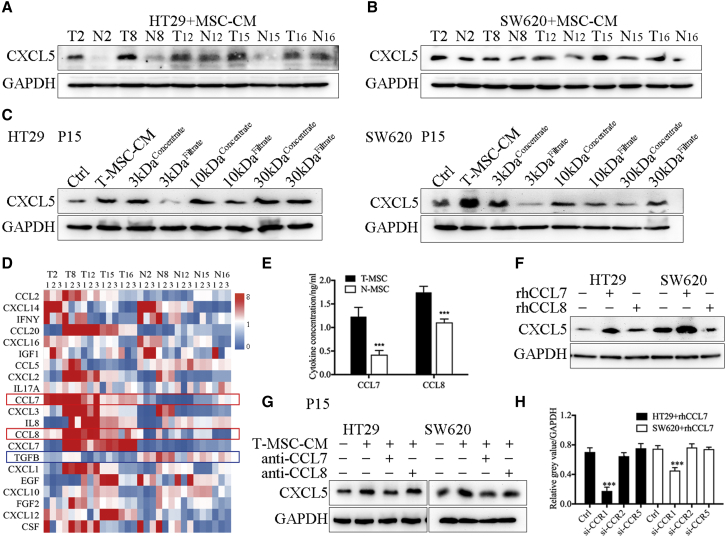
Figure 3.
T-MSCs promoted the expression of CXCL5 in CRC cells by secreting CCL7
(A and B) The results of western blot. T-MSC-CM promoted the expression of CXCL5 in HT29 and SW620. The MSCs showed in the figure were derived from patients P2, P8, P12, P15, and P16. (C) HT29 and SW620 were treated with product of centrifugal filtration, and 3 kDa concentrate and 30 kDa filtrate enhanced the expression of CXCL5. The MSCs showed in the figure were derived from patient P15. (D) The results of qPCR showed the RNA expression of related cytokine in paired MSCs. The MSCs showed in the figure were derived from patients P2, P8, P12, P15, and P16. (E) The results of ELISA. T-MSCs secreted high levels of CCL7 and CCL8. The MSCs showed in the figure were derived from patients P2, P8, P12, P15, and P16. (F) The results of western blot. Expression of CXCL5 was increased in rhCCL7-treated HT29 and SW620 cell lines. (G) The results of western blot. Anti-CCL7 antibody neutralized the CXCL5 promotion effect of T-MSC-CM. The MSCs showed in the figure were derived from patient P15. (H) The results of western blot. Knocking down CCR1 decreased the expression of CXCL5 induced by rhCCL7. Data represent the mean ± SD. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.