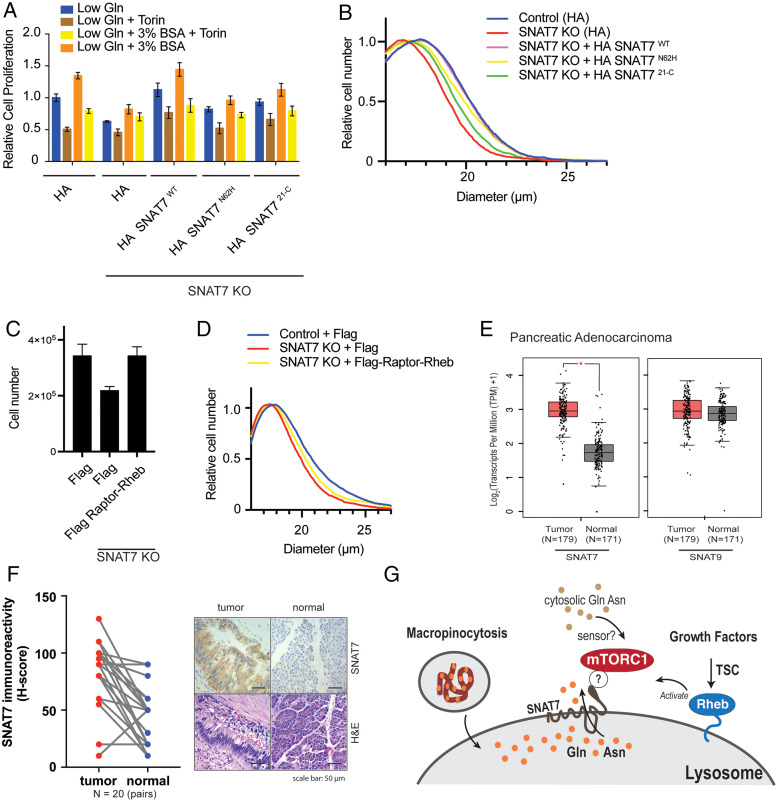
Fig. 4.
SNAT7 regulates pancreatic cancer cell growth through mTORC1. (A) SNAT7 depletion inhibits BSA-induced mTORC1 activation and cell proliferation in pancreatic cancer cell lines. Relative cell proliferation was determined for WT MIA PaCa-2 cells, SNAT7 KO, SNAT7 KO MIA PaCa-2 cells expressing HA-tagged SNAT7WT, HA-tagged SNAT7N62H, or HA-tagged SNAT721-C in low glutamine (Gln) with or without Torin, or low Gln + 3% BSA with or without Torin for 24 h. P values: WT Gln vs. WT Gln + BSA, P < 0.001; WT Gln vs. SNAT7 KO Gln, P < 0.001; WT Gln vs. SNAT7 KO Gln + BSA, P < 0.05; WT Gln vs. HA-SNAT7WT Gln, not significant; WT Gln vs. HA- SNAT7WT Gln + BSA, P < 0.01; WT Gln vs. HA-SNAT7N62H Gln, P < 0.01; WT Gln vs. HA-SNAT7N62H Gln + BSA, not significant; WT Gln vs. HA-SNAT721-C Gln, not significant; WT Gln vs. HA-SNAT721-C Gln + BSA, not significant; WT Gln + BSA vs. SNAT7 KO Gln + BSA, P < 0.001; WT Gln + BSA vs. HA- SNAT7WT Gln + BSA, not significant; WT Gln + BSA vs. HA-SNAT7N62H Gln + BSA, P < 0.001; WT Gln + BSA vs. HA-SNAT721-C Gln + BSA, P < 0.05; SNAT7 KO Gln vs. HA-SNAT7WT Gln, P < 0.001; SNAT7 KO Gln vs. HA-SNAT7N62H Gln, P < 0.01; SNAT7 KO Gln vs. HA-SNAT721-C Gln, P < 0.001; SNAT7 KO Gln + BSA vs. HA-SNAT7WT Gln + BSA, P < 0.001; SNAT7 KO Gln + BSA vs. HA-SNAT7N62H Gln + BSA, not significant; and SNAT7 KO Gln + BSA vs. HA-SNAT721-C Gln + BSA, P < 0.01. (B) SNAT7 depletion inhibits cell growth in pancreatic cancer cell lines. The cell size of control, SNAT7 KO, SNAT7 KO expressing HA-tagged SNAT7WT, SNAT7 KO expressing HA-tagged SNAT7N62H, or SNAT7 KO expressing HA-tagged SNAT721-C MIA PaCa-2 cells were analyzed after 48 h in low glutamine with 3% BSA condition. P values: control vs. SNAT7 KO, P < 0.001; control vs. HA-SNAT7WT, not significant; control vs. HA-SNAT7N62H, P < 0.01; control vs. SNAT7 KO, P < 0.01; SNAT7 KO vs. HA- SNAT7WT P < 0.001; SNAT7 KO vs. HA-SNAT7N62H, P < 0.001; and SNAT7 KO vs. HA-SNAT721-C, P < 0.01. (C) Targeting mTORC1 to the lysosome rescues cell proliferation when SNAT7 is depleted. Cell proliferation was analyzed in WT MIA PaCa-2 cells (control), SNAT7 KO, or SNAT7 KO cells expressing Flag-tagged Raptor-Rheb. P values: control vs. SNAT7 KO, P < 0.01 and SNAT7 KO vs. SNAT7 KO expressing Flag-tagged Raptor-Rheb, P < 0.01. (D) Targeting mTORC1 to the lysosome partially rescues cell size when SNAT7 is depleted. Cell size was measured for WT MIA PaCa-2 cells (control), SNAT7 KO, or SNAT7 KO cells expressing Flag-tagged Raptor-Rheb 48 h after seeding. P values: control vs. SNAT7 KO, P < 0.01 and SNAT7 KO vs. SNAT7 + Flag-Raptor-Rheb, P < 0.05. (E) Expression of SNAT7 is elevated in pancreatic adenocarcinomas. mRNA expression of SNAT7 or SNAT9 in pancreatic adenocarcinomas was analyzed at the GEPIA platform based on TCGA and GTEx dataset. TPM, transcripts per million. *q < 0.001, ANOVA analysis followed by Benjamini and Hochberg false discovery rate correction. (F) SNAT7 protein expression is up-regulated in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma tissues. SNAT7 protein expression was analyzed by immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining in 20 pairs of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma tissues. (Left) Immunoreactivity scores (H-score) was calculated based on percentage and intensity of staining (see Materials and Methods for details). Statistical analysis was performed by paired Student’s t test. P < 0.0001. (Right) Representative staining images of IHC and corresponding hematoxylin and eosin staining are also shown for tumor and normal samples as indicated. (G) Working model of glutamine (Gln) and asparagine (Asn) signaling pathway to mTORC1. Macropinocytosis engulfs proteins, such as albumin where it is targeted to the lysosome and degraded by proteolysis. Then lysosomal amino acids, specifically Gln and Asn, are exported out of the lysosome into the cytoplasm by SNAT7. Cytosolic Gln and Asn (from macropinocytosis or intracellular/extracellular stores) can then activate mTORC1 through an unknown sensor(s). Growth factors activate mTORC1 through tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC)-Rheb signaling axis. ? denotes that another protein may bridge the SNAT7-mTORC1 interaction.