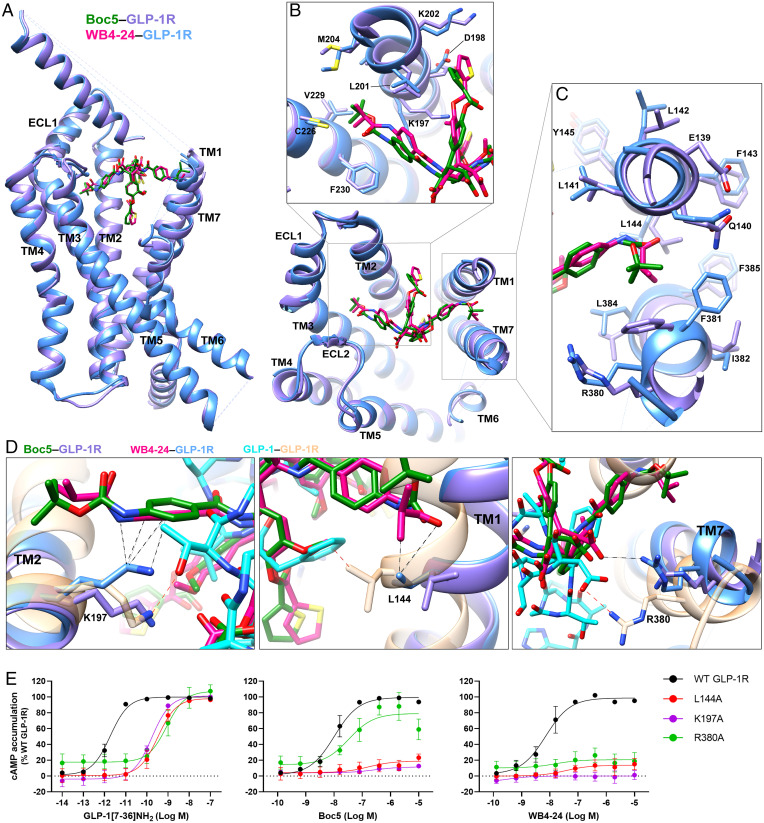
Fig. 3.
Comparison of GLP-1R conformation and ligand binding pocket stabilized by Boc5 and WB4-24. (A) Overlay of Boc5- and WB4-24–bound GLP-1R structures. (B and C) Close-up of the TM bundles viewed from the extracellular side reveals conformational differences in TM2/TM3 (B) and TM1/TM7 (C) backbones when stabilized by different arms of Boc5 and WB4-24. (D) WB4-24 makes more extensive contacts with TM bundles than Boc5 by interacting with residues L144, K197, and R380, which contribute to the agonism of GLP-1. Coloring for A–D denotes the segments as highlighted (GLP-1 in cyan, GLP-1–bound GLP-1R in sandy brown, Boc5 in dark green, Boc5-bound GLP-1R in purple, WB4-24 in magenta, WB4-24–bound GLP-1R in dodger blue). The interactions of the residues with WB4-24 and GLP-1 are indicated by black and red dashed lines, respectively. (E) Mutagenesis analysis of residues L144, K197, and R380 for GLP-1, Boc5, and WB4-24 show the requirement of these contacts for receptor activation. Data are shown as means ± SEM from at least three independent experiments.