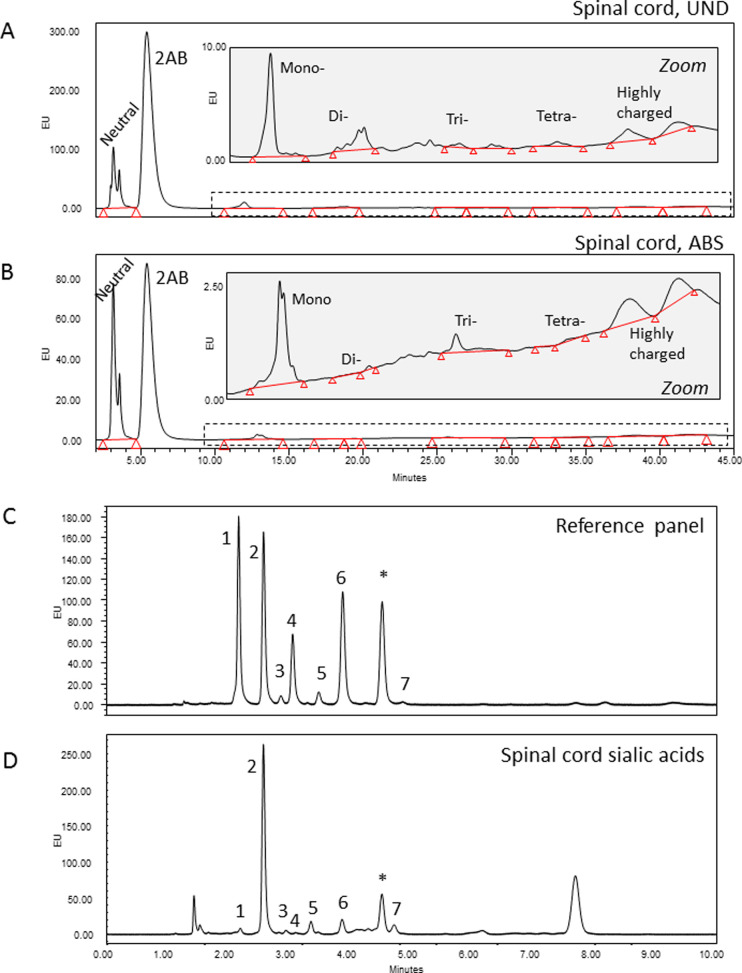
Figure 3.
Sialic acids of rat spinal cord. WAX-HPLC separates glycans on the basis of charge, and fetuin-N was used as a reference standard. Neutral N-glycans (77%); mono-charged (12%); di-charged (4%); tri-charged (1%); tetra-charged (1%); unidentified highly charged N-glycan species (5%); 2AB, excess 2AB label; (A) UND, undigested; (B) ABS, ABS (sialidase) digested. The dashed line indicates the zoomed region. (C) Reference standard for DMB analysis. (D) Neu5Ac is the most common type of sialic acid in the rat spinal cord, with minor amounts of Neu5Gc- and Neu5xAc2-type sialic acids. Sialic acids were released from spinal cord glycans by hydrolysis and separated on the basis of chemical structure. Peak 1, Neu5Gc; peak 2, Neu5Ac; peak 3, Neu5,7Ac2; peak 4, Neu5Gc9Ac; peak 5, Neu5,8Ac2; peak 6, Neu5,9Ac2; and peak 7, Neu5,x,xAc3, where x is an unknown position; * contaminant peak. Note that DMB analysis was performed on total spinal cord glycans, and WAX-HPLC on N-glycans.