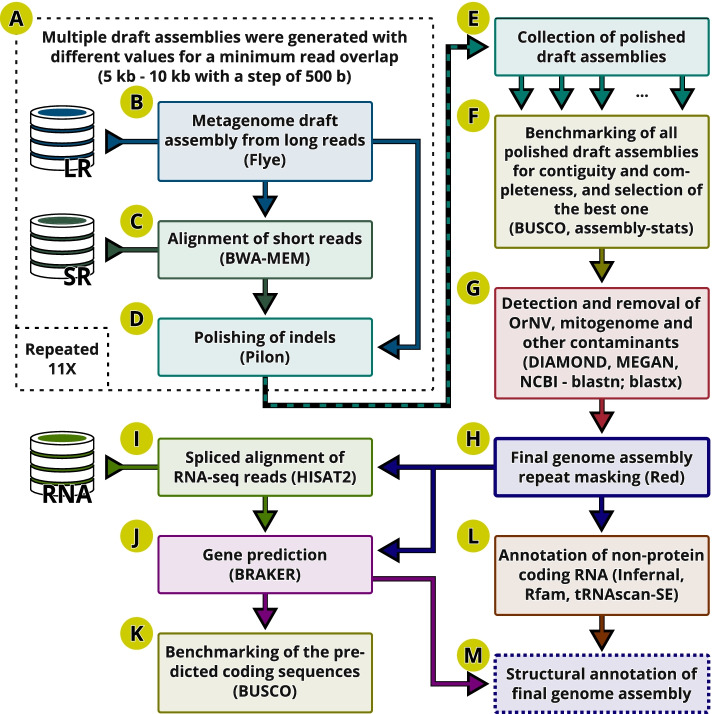
Fig. 3.
Iterative assembly refinement. (A) Multiple polished draft assemblies are generated (B-D), collected (E) and benchmarked for completeness and contiguity (F) to determine the optimal read overlap for the long leads [LR]. (G) Optimal draft assembly is screened for potential contaminants. (H) The repeats are detected and soft masked. The splice-aware alignments (I) of the RNAseq datasets [RNA] are used for gene prediction (J), and then assessed for completeness (K). Annotations of the non-protein coding RNAs (L) are added to form the final structural annotation (M)