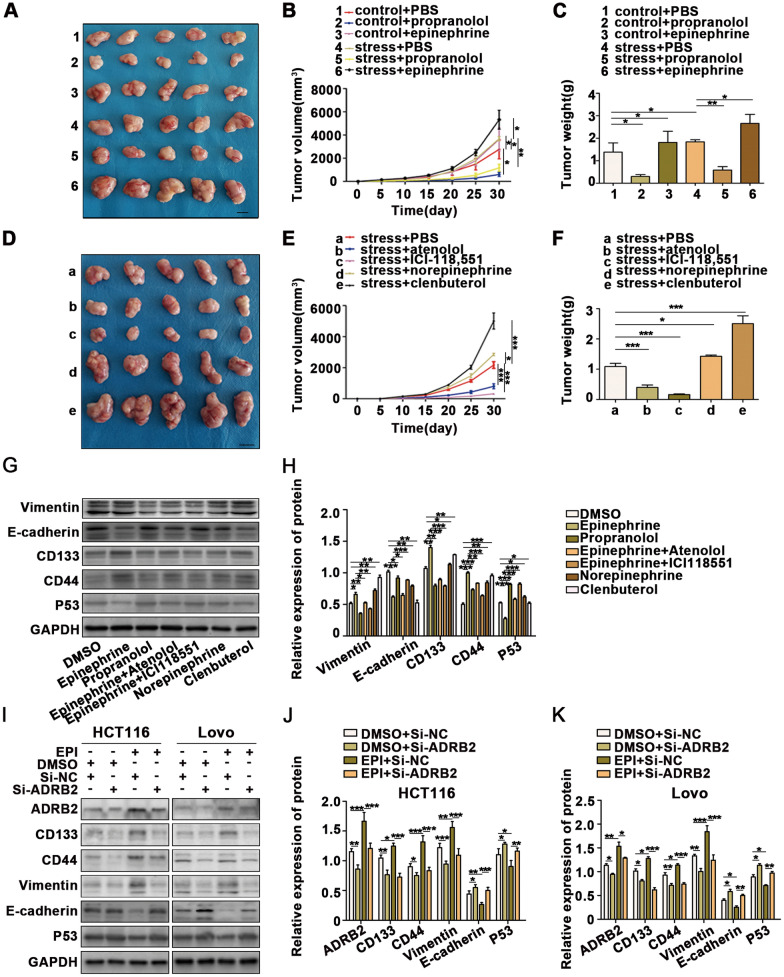
Fig. 3.
Chronic stress promotes the development of colon cancer via the epinephrine-ADRB2 axis. A–C CT26-inoculated BALB/C mice were treated with PBS, propranolol, and epinephrine added to the drinking water. Another four groups of mice were treated with chronic stress combined with drug treatments (1: control + PBS, 2: control + propranolol, 3: control + epinephrine, 4: stress + PBS, 5: stress + propranolol, and 6: stress + epinephrine, scale bar: 1 cm). D–F CT26 cells were inoculated into the right flanks of BALB/C mice 30 days after initiating stress, and the mice were subsequently treated with PBS, atenolol, ICI-118,551, norepinephrine, and clenbuterol added to the drinking water (a: stress + PBS, b: stress + atenolol, c: stress + ICI-118,551, d: stress + norepinephrine, and e: stress + clenbuterol, scale bar: 1 cm). G-H HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO, EPI, propranolol, EPI + atenolol, EPI + ICI118,551, norepinephrine, and clenbuterol. The expression of EMT and CSC markers was detected by WB. I–K WB analysis revealed that knocked down ADRB2 expression effectively reverses EPI-induced CRC progression of EMT and CSCs. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001