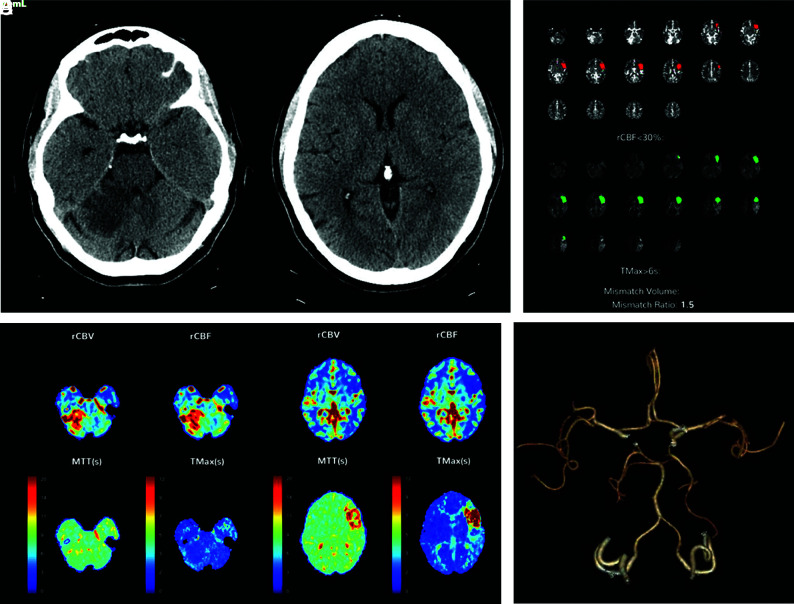
FIG 2.
A patient presenting with an acute left MCA syndrome. CT also demonstrates an acute/subacute right superior cerebellar infarct (A and B). CT perfusion was performed and reconstructed using both manual (Advantage Workstation, not shown) and automated (C–E) perfusion software and demonstrates similar results. The quantitative perfusion maps demonstrate acute left MCA ischemia but no evidence of core infarct in the right superior cerebellar hemisphere (C). D and E, Qualitative color maps demonstrate elevated CBF and CBV in the right superior cerebellar infarct, consistent with reperfusion. CTA also demonstrates the right superior cerebellar artery to be patent and the M2 segment of the left MCA to be occluded (F). rCBF indicates relative CBF; rCBV, relative CBV; Tmax, time-to-maximum.