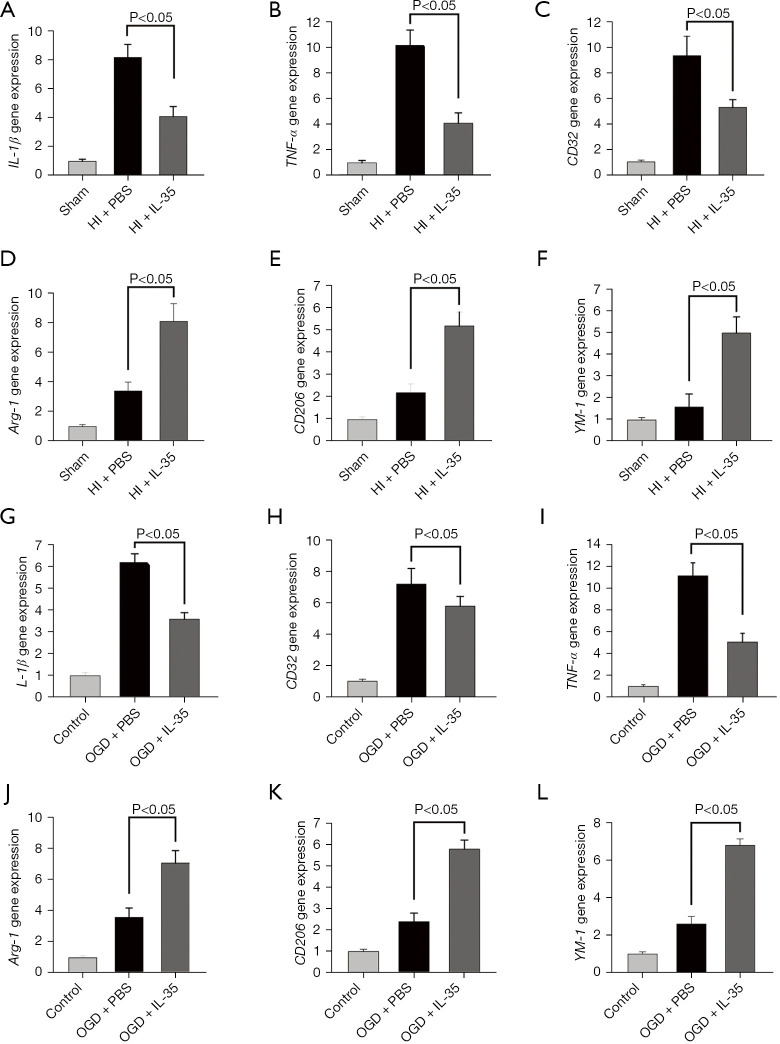
Figure 2.
IL-35 treatment suppressed M1 microglial polarization after HI injury. Intraperitoneal injection of IL-35 (20 µg/g BW) in HIE pups immediately and 24 h post HI. Microglial polarization was assessed at 48 h following HI insult. (A-C) M1 markers (IL-1β, TNF-α, and CD32) were assessed by RT-qPCR analysis; (D-F) M2 markers (Arg-1, CD206, and YM-1) were assessed by RT-qPCR analysis. n=6 in each group. Error bars represent the mean ± SD. BV2 cells were cultured with IL-35 (20 ng/mL) for 6 h and then subjected to 6 h OGD and 24 h reoxygenation; (G-I) M1 markers (IL-1β, CD32, and TNF-α) were assessed at 24 h post-reoxygenation by RT-qPCR analysis; (J-L) M2 markers (Arg-1, CD206, and YM-1) were assessed 24 h post-reoxygenation by RT-qPCR analysis. Error bars represent the mean ± SD of at least 3 independent experiments. IL, interleukin; HIE, hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy; RT-qPCR, real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction; OGD, oxygen-glucose deprivation; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; Arg-1, arginase-1; Ym-1, chitinase-like protein 3; BW, body weight; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; HI, hypoxic ischemia.