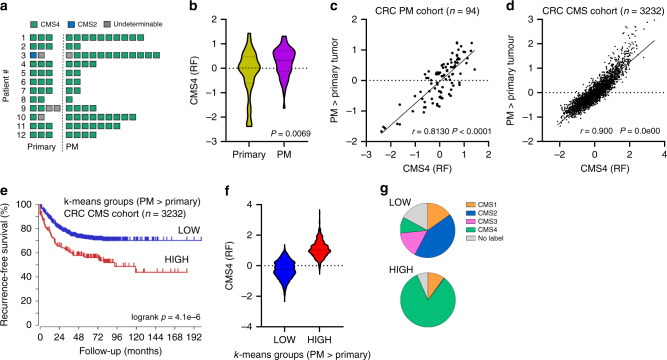
Fig. 2. PM and the primary tumours from which they arise represent an almost uniform CMS4 entity within CRC.
a Application of the CMS classifier on the RNAseq data reveals strong enrichment of CMS4. b Expression of the genes positively identifying CMS4 in the original CMS random forest classifier (CMS4 (RF); 143 genes) in PM and primary tumour samples. c Differential gene expression analysis identified 366 genes that were significantly higher expressed in PM than in paired primary tumour samples. The scatter plot shows the correlation of meta-gene expression values of this gene set in relation to the CMS4-identifying gene set (CMS4 (RF)). d As in (c), but in the original composite CMS cohort (n = 3232 primary tumours). e k-means clustering of the CMS cohort using the 366 PM-enriched gene set shows a correlation between high expression of this ‘PM-signature’ and a significantly shorter recurrence-free survival. f Expression of CMS4-identifying genes from the RF classifier in the k-means groups generated with the PM signature. g Distribution of CMS subtypes in the k-means groups generated with the PM signature.