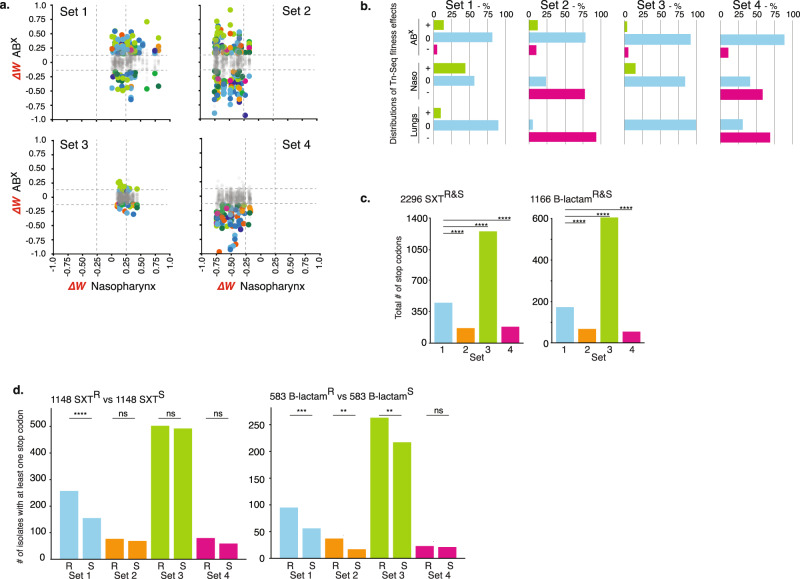
Fig. 8. Stop codons are enriched in clinical samples in Tn-Seq predicted tolerome genes.
a Based on in vivo and ABX Tn-Seq data, four gene sets consisting of 34 genes each were compiled with specific fitness profiles in the presence of antibiotics and in vivo. Shown are the in vivo effects for nasopharynx, while lung data are depicted in Supplementary Fig. 5. ΔW represents the fitness difference of a gene in a specific condition (e.g., an antibiotic, in vivo) minus its fitness in vitro in rich medium. Dashed lines indicate significance cut-offs, grayed-out dots indicate genes with no significant change in fitness in the presence of antibiotics, colors represent antibiotics and are the same as in Fig. 1. b Detailed distributions for each gene set highlight whether effects in the presence of antibiotics, in the nasopharynx and lungs increase (+), do not affect (0) or decrease (−) relative fitness. Gene set rationales are described in the text. c The total number of stop codons in each gene set for 2296 co-trimoxazole and 1166 β-lactam resistant and sensitive strains. d The number of sensitive and resistant strains with at least one stop codon in a gene in each gene set. Significance is measured through a Fisher’s exact test: **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.