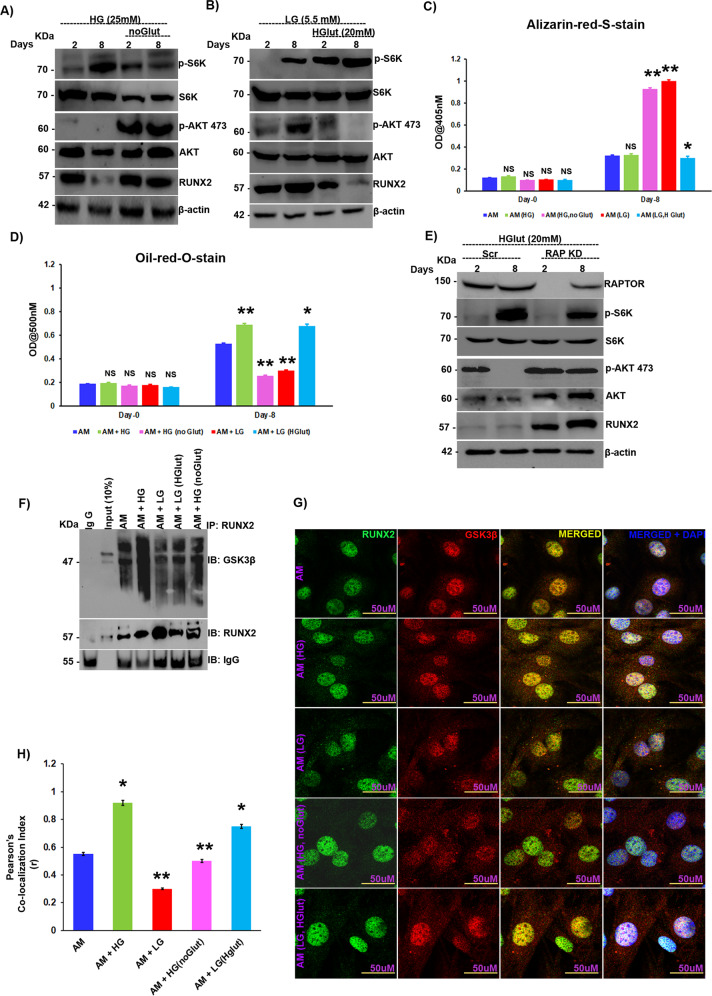
Fig. 5. High glucose-induced glutamine sparing triggers RUNX2 loss under diabetic conditions.
Murine MSCs (C3H10T1/2) were subjected to adipogenic differentiation A in the presence of high glucose (25 mM) with or without glutamine (4 mM) and B in the presence of low glucose (5.5 mM) with or without high glutamine (20 mM) followed by Western blot analysis at the indicated intervals. C Quantification of alizarin red S staining by spectrophotometry. D Quantification of oil red O staining by spectrophotometry. Murine MSCs (C3H10T1/2) were subjected to adipogenic differentiation in the presence of high glutamine (20 mM) with or without raptor siRNA, and cell lysates were subjected to E Western blot analysis as indicated. F Immunoprecipitation analysis of murine MSCs (C3H10T1/2) induced to adipogenic differentiation under varying glucose and glutamine concentrations. Anti-RUNX2 complexes were pulled and immunoblotted with anti-GSK3β and anti-RUNX2 antibodies. G Confocal images of murine MSCs (C3H10T1/2) induced to adipogenic differentiation under varying glucose and glutamine concentrations for 8 days, stained with anti-RUNX2 (Alexa 488) and anti-GSK3β (Alexa 594) and counterstained with DAPI (400). H Quantification of confocal images by ImageJ software. Mean ± S.E.M.; N = 3, *p < 0.1 versus control, **p < 0.01 versus control; NSp > 0.1 versus control. Glut glutamine, HGlut high glutamine, AM adipogenic medium, LG low glucose, HG high glucose, IP immunoprecipitation, IB immunoblotting, NS not significant.