FIGURE 1.
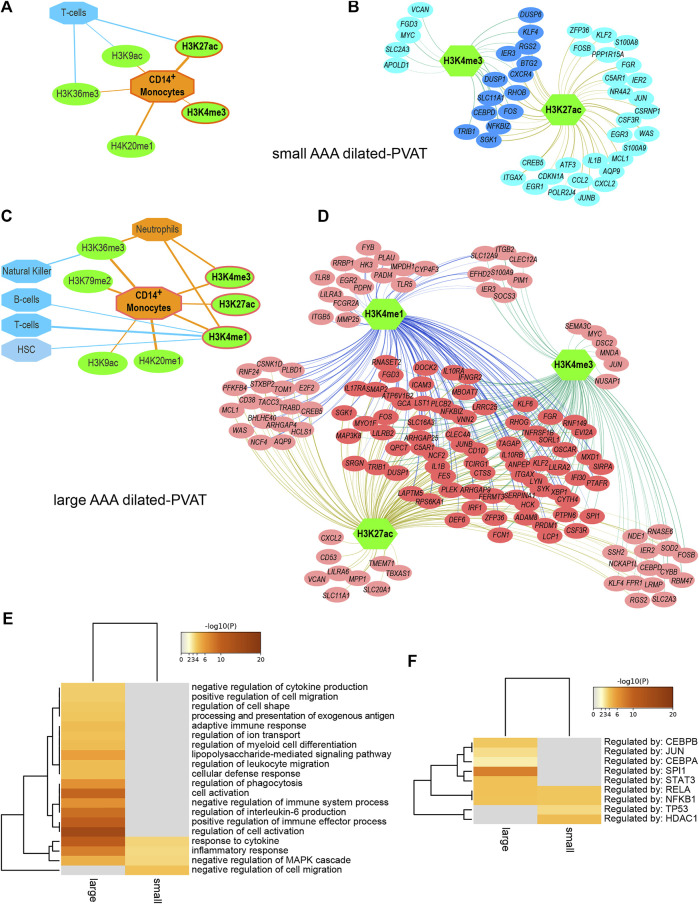
Regulatory networks and functional enrichment analysis of genes overexpressed in AAA dilated-PVAT related to immune cells and functions (A) Predicted histone modifications (green ovals) significantly associated with transcriptionally active euchromatin of myeloid or lymphoid immune cells (orange and blue octagons, respectively) in small AAA dilated-PVAT. The histone mark signature recalling immune response after acute stimulation is highlighted with an orange border. In this and panel C, edge thickness is proportional to the normalized enrichment score, which measures the relevance of enrichment (B) Regulatory network of histone marks and genes overexpressed in dilated-PVAT linked to acute stimulation in early-stage AAA (small AAA). Green hexagons represent histone marks associated with CD14+ monocytes, blue ovals show associated genes. Overexpressed genes associated with this histone mark signature are highlighted in dark blue (C) Predicted histone modifications significantly associated with myeloid or lymphoid immune cells in large AAA dilated-PVAT. The histone mark signature recalling trained immunity is outlined in orange (D) Regulatory network of histone marks and genes overexpressed in dilated-PVAT linked to trained immunity in advanced AAA (large AAA). Green hexagons are as in panel B, pink ovals show associated genes. Overexpressed genes associated with this histone signature are highlighted in dark pink (E) Functional enrichment of Gene Ontology (GO) biological processes and (F) transcription factors relative to overexpressed genes associated with acute stimulation or trained immunity. The ochre to brown color gradient indicates the significance level of the GO terms expressed as -log10 of the adjusted p-values; gray color indicates non-significant associations. Significant terms were hierarchically clustered based on the Kappa score.