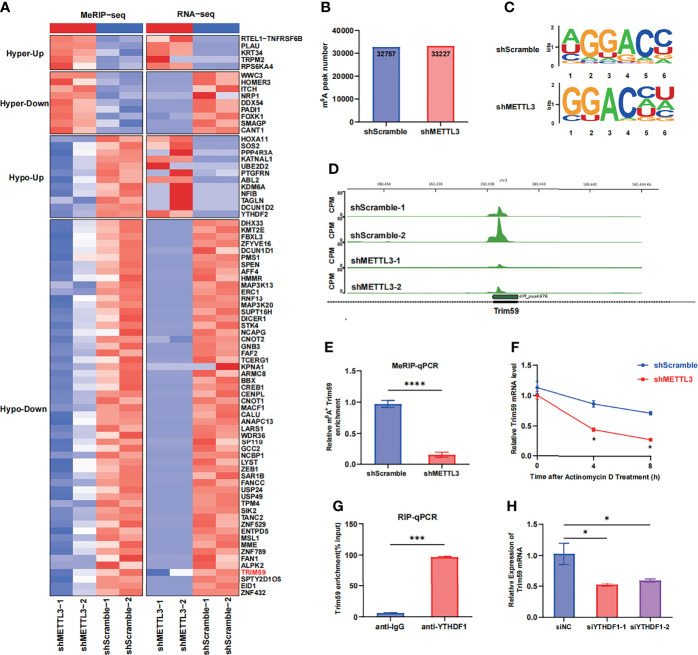
Figure 4.
METTL3-mediated m6A modification of Trim59 mRNA maintains its YTHDF1-dependent stability (A) Heatmap showing the clusters with significant changes in both the RNA expression level (RNA-seq) and m6A level (MeRIP-seq) in scramble and METTL3 shRNA-treated HULEC-5a cells. (B) Number of m6A peaks in scramble and METTL3 shRNA-treated HULEC-5a cells. (C) Global profiling of m6A in HULEC-5a cells and the sequence motif identified from the top 1000 m6A peaks. (D) MeRIP-seq plotted the m6A abundances on Trim59 mRNA transcripts in HULEC-5a cells. (E) MeRIP-qPCR examined METTL3-mediated Trim59 mRNA m6A modifications. (F) RT-qPCR analysis showing the levels of Trim59 expression in METTL3-downregulated HULEC-5a cells treated with actinomycin D (2 μg/mL) at the indicated time points. (G) RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP)-qPCR assay showing the enrichment of YTHDF1 binding to Trim59 m6A modification sites. (H) RT-qPCR analysis showing the levels of Trim59 expression in YTHDF1-knockdown HULEC-5a cells. All data are expressed as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.