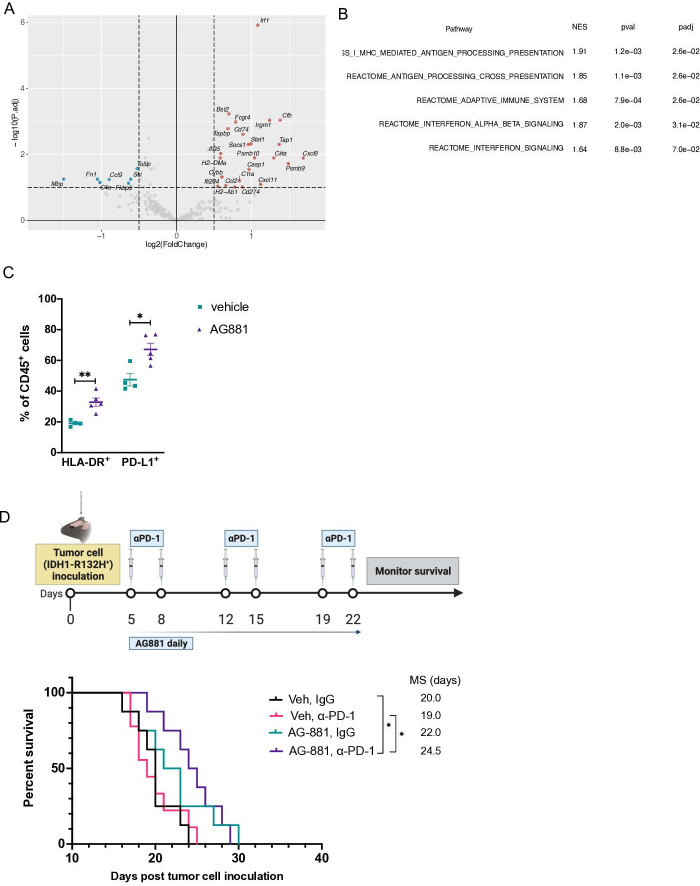
Figure 6.
Inhibition of IDH1R132H function in vivo results in an enhanced IFNɣ signature response and therapeutic efficacy of PD-1 blockade. (A) Mice bearing dTG-IDH1R132H tumors were treated with vehicle (n=3) or 10 mg/kg AG-881 (n=3) for 14 days. mRNA from tumor samples was collected and analyzed using the Mouse Immunology v2 panel (Nanostring) for significant changes in gene expression resulting from IDH1R132H inhibition. (B) The top 5 (out of 136 gene sets) significantly upregulated pathways following AG-881 treatment. (C) CD45+ single-cell suspensions derived from the dTG-IDH1R132H tumors of mice treated as in (A) were analyzed by FC for the expression of HLA-DR and PD-L1. *P<0.05, **p<0.002; Student t-test. (D) Schematic representation of the combined AG-881 and PD-1 blockade treatment protocol and Kaplan-Meier survival curves. Vehicle control and isotype antibody (Veh, IgG; n=8), vehicle and PD-1 blocking antibody (Veh, α-PD-1, n=9), AG-881 and isotype antibody (AG-881, IgG; n=9), AG-881 and PD1 blocking antibody (AG-881, α-PD-1, n=8). *p<0.05; long-rank test. dTG, double transgenic; HLA, human leukocyte antigens; NES, normalized enrichment score; padj, adjusted p values.