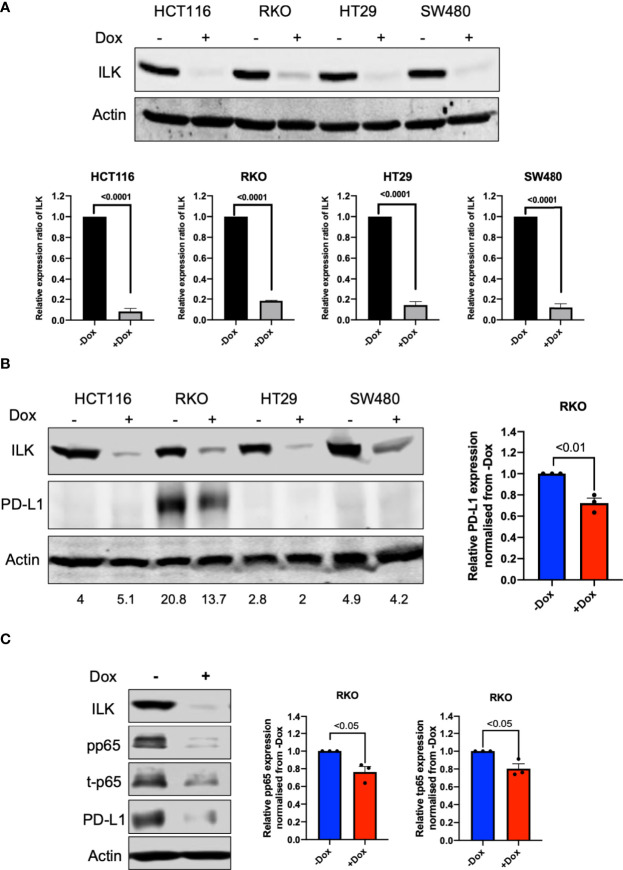
Figure 9.
ILK KD reduced basal PD-L1 expression in RKO CRC cells via NF-κB p65 regulation. [(A), upper] Western blot showing expression of ILK protein. [(A), lower] Quantitation of ILK protein, the means were normalized to -Dox (n = 3). Cells were seeded into a 6-well culture plate and duplicated into 2 sub-populations and incubated overnight. One sub-population per cell line was treated with 2 µg/ml doxycycline to induce CRISPR/Cas9 to delete the ILK gene over 3 days. The doxycycline was washed from the cells and the cells sub-cultured for growing. The cells were then harvested for testing ILK protein expression via western blot and the Dox-treated cells are verified as ILK KD cells. (B) The western blot of PD-L1 protein expression in CRC cell lines at the basal level. (C) ILK KD reduced NF-κB p65/PD-L1 protein expression in the RKO CRC cell line. (left) The western blot showed the effect of ILK KD in RKO cells on PD-L1 and NF-κB p65 (total and phosphorylated) protein expression at 4 hr serum stimulation following overnight starvation. (right) The quantitation of PD-L1, p65 phosphorylation (pp65) and p65 total protein expression (t-p65). Quantitation of protein expression normalized to -Dox. Actin was used as an internal control. Error bars are represented as mean ± SEM (n = 3). P-value was analyzed with an unpaired t-test. The significant P-value is < 0.05.