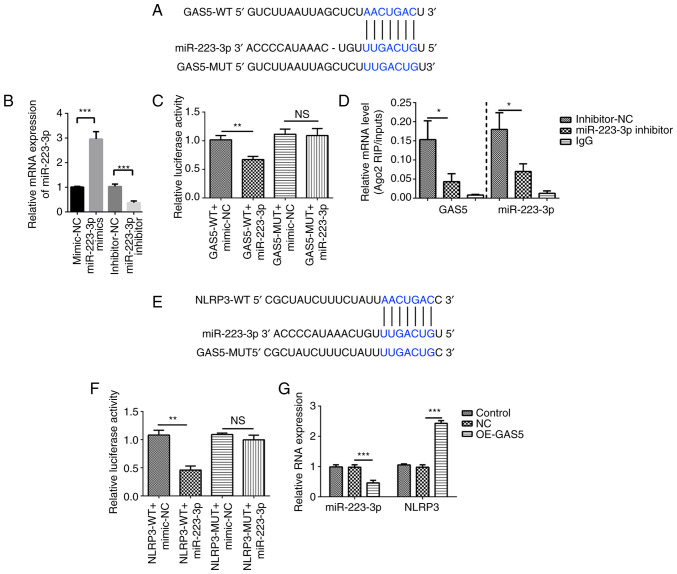
Figure 4.
GAS5 targets the miR-223-3p/NLRP3 axis. (A) Bioinformatics analysis was used to predict the binding site of GAS5 to miR-223-3p. (B) Transfection efficiency of miR-223-3p mimics and inhibitor was analyzed using qPCR. (C) GAS5 binds to the putative target sites of miR-223-3p as verified using a luciferase assay. (D) RIP assay followed by qPCR was used to determine GAS5 and miR-223-3p expression. (E) Bioinformatics analysis was used to predict the binding site of miR-223-3p to NLRP3. (F) miR-223-3p binds to the putative target sites of NLRP3 as verified using a luciferase assay. (G) Expression levels of miR-223-3p and NLRP3 in GAS5-overexpressing MRC-5 cells were measured using qPCR. The results are presented as the mean ± SD (n=3; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs. control). GAS5, growth arrest-specific 5; NLRP3, NLR family pyrin domain containing 3; miR-223-3p, microRNA 223-3p; 3′ UTR, 3′ untranslated region; Ago2, argonaute RISC catalytic component 2; OE, overexpression; NC, GAS5 overexpression negative control lentivirus vectors; RIP, RNA immunoprecipitation; qPCR, quantitative PCR; WT, wild-type; MUT, mutant; NS, no significant difference.