Figure 4.
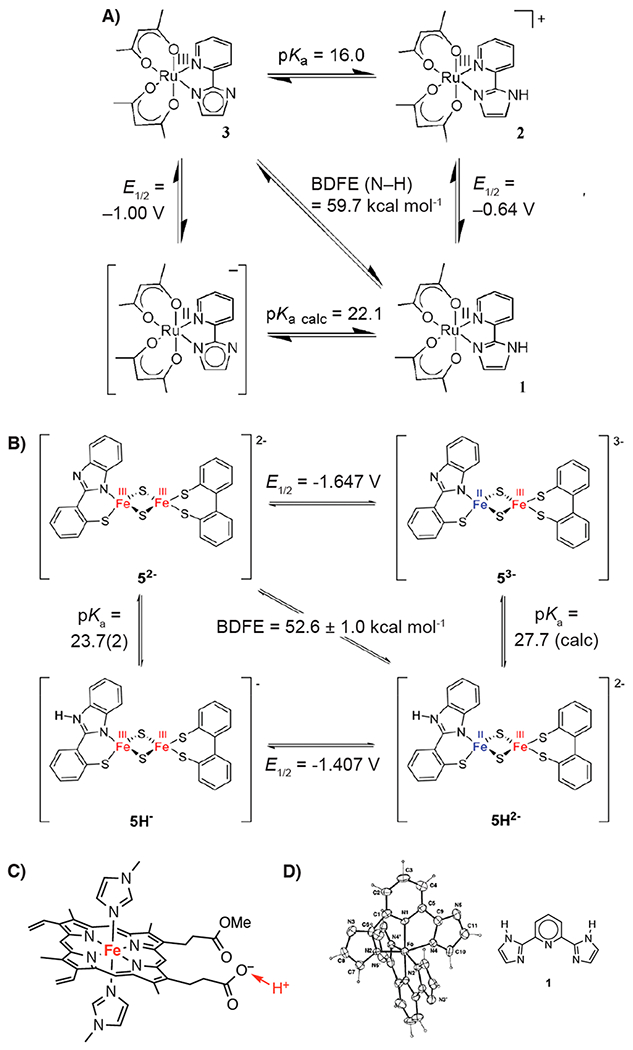
Imidazole and other complexes with an acid/base group removed from the redox-active metal center. (A) Square scheme for a ruthenium–imidazole complex showing the 0.36 V increase in the reduction potential upon protonation. Reprinted (adapted) with permission from ref 82. Copyright 2007 American Chemical Society. (B) Square scheme for a di-iron disulfido–benzimidazole complex showing a 0.240 V increase upon protonation. Reprinted with permission from ref 83. Copyright 2017 American Chemical Society. BDFEs in A and B were updated to reflect the new CG(MeCN) value. (C) An iron–protoporphyrin-IX complex that shifts 20 mV upon protonation at the carboxylate. Reprinted with permission from ref 86. Copyright 2011 American Chemical Society. (D) Drawing of the structure of the Fe(III) complex with two doubly deprotonated bis(imidazolyl)pyridine ligands, [Fe(1–2H)2]−.84,85 Reprinted with permission from ref 84. Copyright 1998 Royal Society of Chemistry.
