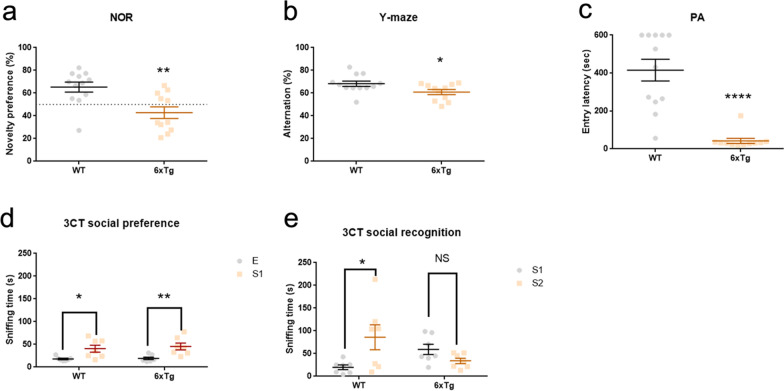
Fig. 3.
Cognitive deficit in 9- to 11-months-old 6xTg mouse model of AD. a 6xTg exhibited reduction in novel object recognition (n = 12 for WT, 11 for 6xTg; Student’s t-test, **p < 0.01). b Spontaneous alternation was significantly decreased in the 6xTg compared with that of WT mice (n = 12 for WT, 11 for 6xTg; Student’s t-test, *p < 0.05). c The latency to enter the shock-associated chamber was significantly decreased in the 6xTg compared with that of WT mice (n = 12 for WT, 10 for 6xTg; Student’s t-test, ****p < 0.0001). d Both the WT and 6xTg mice showed significantly longer sniffing time for the stranger 1 than for the empty cage (n = 7 for WT, 7 for 6xTg; Two-way ANOVA, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). e WT mice preferred stranger 2, whereas the 6xTg mice did not show preference towards the social novelty (n = 7 for WT, 7 for 6xTg; Two-way ANOVA, *p < 0.05). In the 3CT, data points from 5 WT mice and 4 6xTg mice were omitted as the animals escaped the behavioral apparatus. All data are given as means ± SEM. E, empty; S1, stranger 1; S2, stranger 2