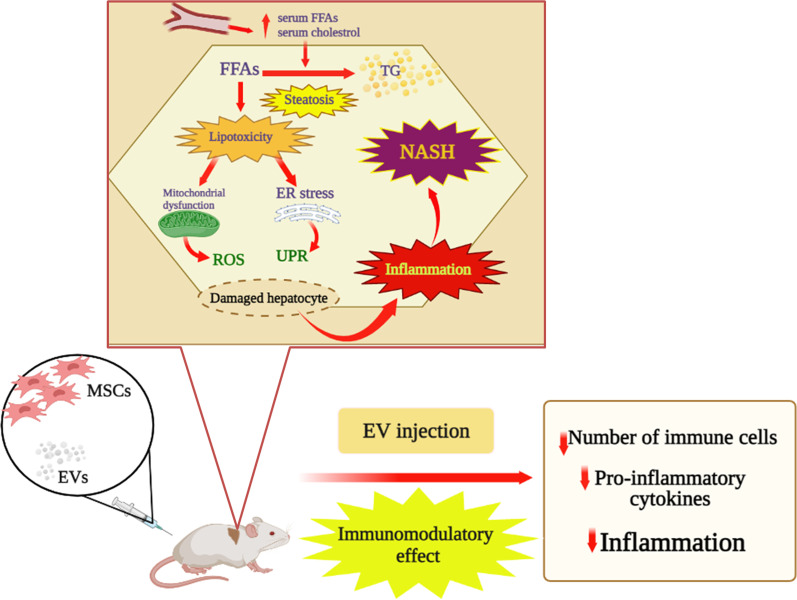
Fig. 1.
Immunomodulatory effect of MSC-EV in liver injury. FFAs, free fatty acids; TG, triglyceride; ROS, reactive oxygen species; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; UPR, unfolded protein response; NASH, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis; MSC, mesenchymal stem cell; EV, extracellular vesicle. The increased hepatic FFAs flux which derives from the multiple hits leads to two different situations: synthesis and accumulation of triglycerides (TG) (steatosis) and ‘toxic’ levels of fatty acids, free cholesterol, and other lipid metabolites (lipotoxicity) which cause mitochondrial dysfunction with oxidative stress and production of ROS and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress with activation of UPR, all leading to hepatic inflammation. In vivo study, immunomodulatory effect of MSC-EVs alleviated inflammation and decreased the number of immune cells and pro-inflammatory cytokines.