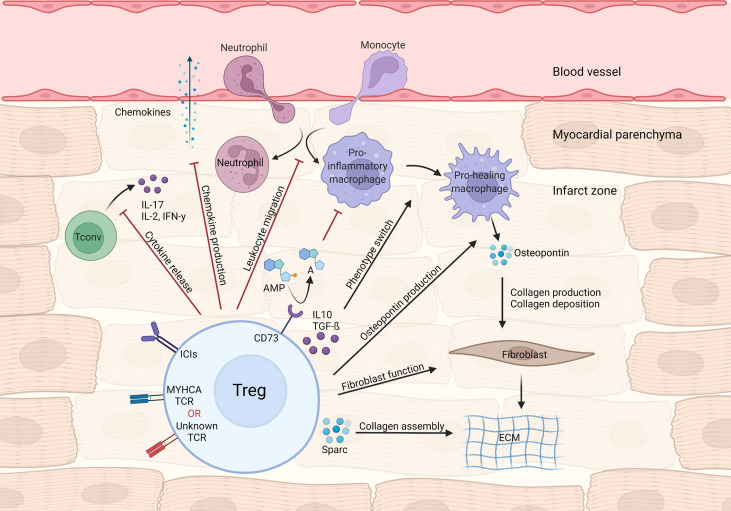
Figure 1.
Treg-mediated effects in myocardial repair and inflammation after infarction. Tregs control local immune responses through a multitude of mechanisms, including inhibiting both canonical TH1/TH17 cytokine production and leukocyte migration. Treg cytokines (e.g. IL-10 and TGF-β) and purinergic metabolism products may modulate macrophage polarization towards a pro-healing/reparative phenotype. In addition, Tregs contribute to fibroblast activation and steady collagen deposition in the infarcted area.