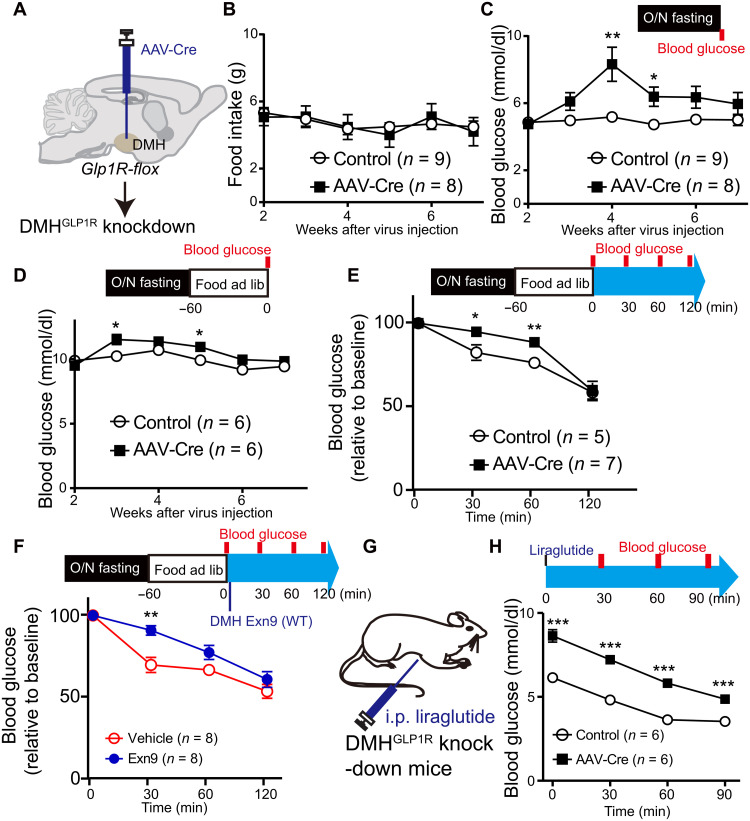
Fig. 3. Ablation of GLP-1R expression in the DMH increases blood glucose level.
(A) Experimental paradigm for viral injection of AAV-Cre in GLP1Rf/f mice. (B) Overnight food intake is not changed during 7 weeks of observation. (C) Fasting blood glucose level increased 4 weeks after GLP-1R depletion from the DMH. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 (repeat measurement with post hoc t test). (D) To monitor the glucose levels under refed condition, GLP1Rf/f mice were fasted overnight and then food was available for 1 hour. Blood glucose was measured after 1-hour refeeding and was shown higher in GLP-1R depletion group (repeat measurement: group effect, P < 0.05; group × time effect, P < 0.05; post hoc ANOVA, *P < 0.05 at weeks 3 and 5). (E) To study the effect of the GLP-1 signal on postprandial glucose, GLP1Rf/f mice were fasted for overnight. Glucose levels were measured right after 1-hour refeeding, t = 0, and then t = 30 and 60 min. GLP-1R depletion group showed higher postprandial glucose level when compared to control group (repeat measurement, group effect, P < 0.05; post hoc ANOVA, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). (F) Exn9 was injected into DMH immediately after 1-hour refeeding in WT mice, and the first time point (t = 0) for glucose level was measured. Then, glucose levels were measured at t = 30 and 60 min. Postprandial glucose significantly increased 0.5 hours after Exn9 injection when compared to vehicle group (repeat measurement, group effect; post hoc ANOVA, P < 0.05; **P < 0.01). (G) Experimental paradigm for GLP-1R agonist liraglutide effect on fasting glucose levels in GLP1Rf/f mice. (H) Fasting blood glucose level decreased in both control and GLP-1R knockdown group after liraglutide injection (repeat measurement, P < 0.001, time effect, P < 0.001, group effect); post hoc ANOVA analysis showed that blood glucose is higher in GLP-1R knockdown group than in control group, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001. n numbers are indicated in each panel.