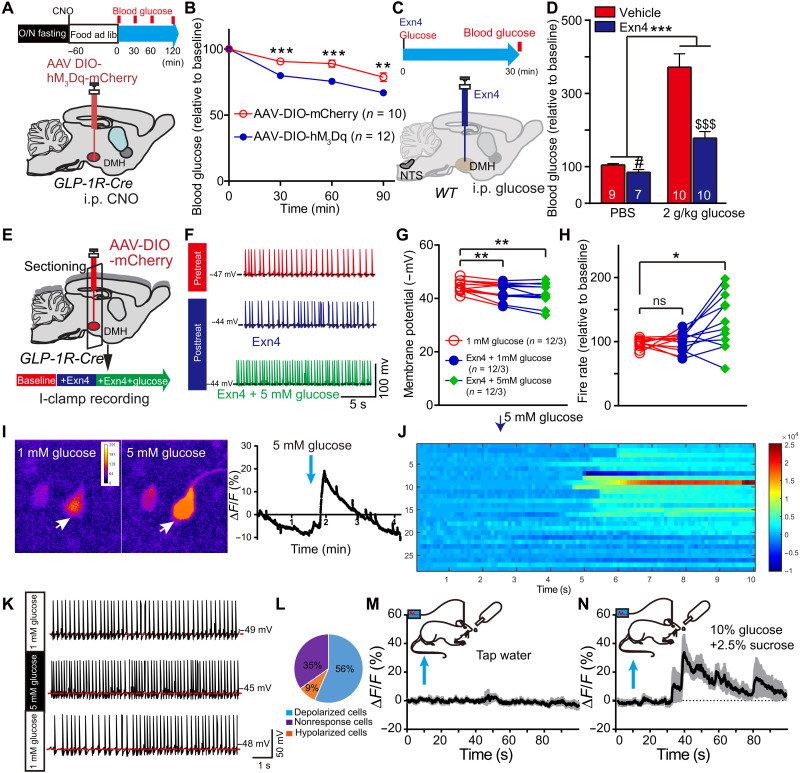
Fig. 5. DMHGLP-1R neurons are glucose sensing.
(A) Experimental paradigm for viral injection in GLP-1R-Cre mice and time schedule for postprandial glucose measurements. (B) Stimulation of DMH GLP-1R neurons significantly decreased blood glucose level when compared to control group in refed condition. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 (ANOVA test). (C) Experimental paradigm for DMH injection with Exn4 and intraperitoneal injection with glucose (2 g/kg) in WT mice. (D) Exn4 decreased blood glucose in both PBS group (#P < 0.05, t test) and 2 g/kg glucose group ($$$P < 0.001, t test). DMH Exn4 showed a greater ability to lower blood glucose after intraperitoneal glucose injection. ***P < 0.001, Exn4 × glucose effect. (E) Experimental paradigm for the investigation of Exn4 effects on GLP-1R neuronal activity. (F) Representative trace for recording I-clamp from GLP-1R neurons. (G) Membrane potential is significantly increased after Exn4 + 1 mM glucose or Exn4 + 5 mM treatment. **P < 0.01 (paired t test; n = 12 cells from three mice). (H) Exn4 + 5 mM but not Exn4 + 1 mM treatment significantly increased firing rate of GLP-1R neurons. *P < 0.05 (paired t test). (I) Representative cell responses of DMH GLP-1R neurons to 5 mM glucose treatment (pointed by white arrow). (J) Overall, 20 of 29 DMH GLP-1R cells (from four mice) showed a significant change in ΔF/F during 5 mM glucose perfusion. (K) Representative trace for recording I-clamp from GLP-1R neurons during perfusion with 5 mM glucose in GLP-1R-Cre mice. (L) Thirteen of 23 neurons sampled were shown to be glucose excitable, while two cells are inhibited by 5 mM glucose perfusion. (M) No significant change in calcium signal for DMH GLP-1R neurons was found during tap water consumption, while a 30% change in fluorescence was observed during intake of a glucose and sucrose solution (n = 4). (N) Data in (M) and (N) are presented at mean with SEM in shadow.