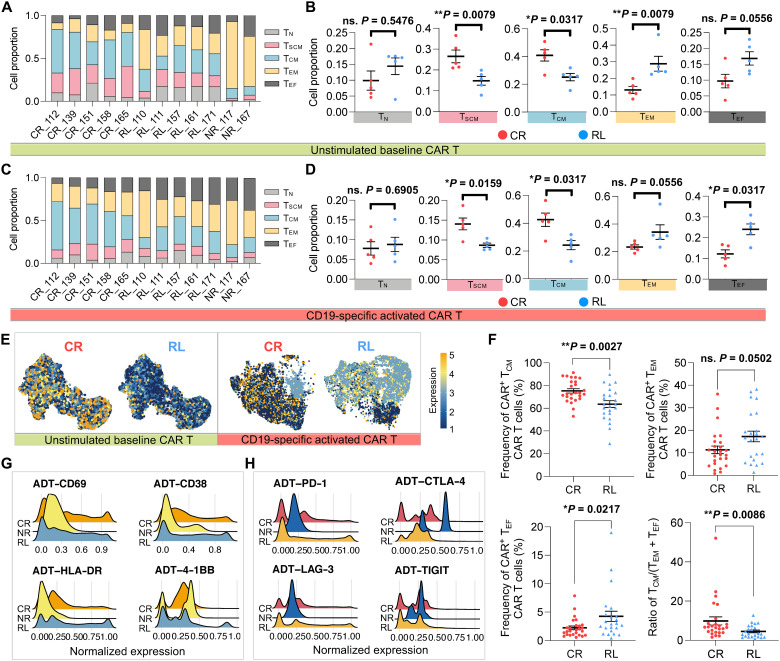
Fig. 6. Phenotypic proteomic profile reveals the dampened capacity of maintaining early memory T cell states in CAR T cells from relapsed patients.
(A) Differential state composition of unstimulated baseline CAR T cells in each patient based on the expression of CD62L, CCR7, CD45RA, and CD45RO from CITE-seq data. TN, naïve; TSCM, stem cell–like memory; TCM, central memory; TEM, effector memory; TEF, effector T cells. The x axis represents responsive state and patient ID. (B) Proportion comparison of unstimulated CAR T cell phenotypic subsets between CR and RL groups. (C) Differential state composition of CD19-specific activated CAR+ cells in each patient. (D) Proportion comparison of activated CAR+ cell phenotypic subsets between CR and RL groups. (E) Feature plot of cellular protein CCR7 expression in unstimulated or activated CAR T cells, split by responsive groups. (F) Frequency of CAR+ cells with different differential states in the expanded validation cohort. (G) Single-cell expression distribution of the T cell activation–related surface protein markers of each group. (H) Single-cell expression distribution of coinhibitory surface protein markers of each group. All P values were calculated with Mann-Whitney test. Scatter plots show means ± SEM.