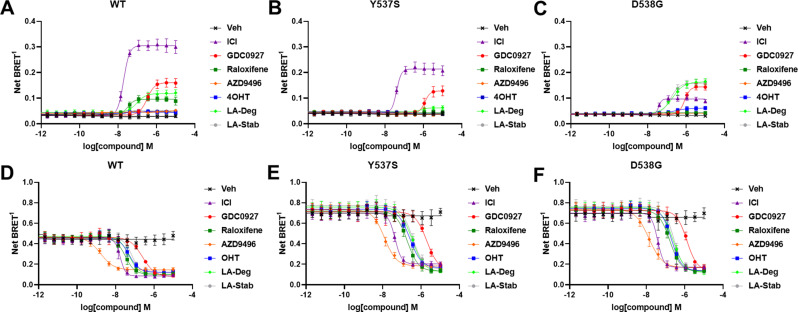
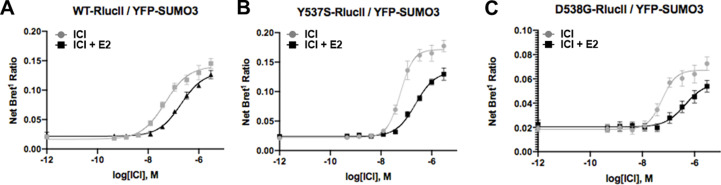
Figure 4. Impact of Y537S and D538G mutation on ligand-induced estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) SUMOylation and SRC1 coactivator binding.
SUMOylation of WT (A), Y537S (B), or D538G (C) ERα in the presence of vehicle, fulvestrant, GDC0927, raloxifene, AZD9496, 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4OHT), lasofoxifene-degrader (LA-Deg), or lasofoxifene-stabilizer (LA-Stab). Data are shown as the mean ± SEM n=3–5 biological replicates. Association of WT (D), Y537S (E), and D538G (F) ERα and the receptor-interacting domain of SRC1. Data are shown as the mean ± SEM, n=3 biologic replicates.