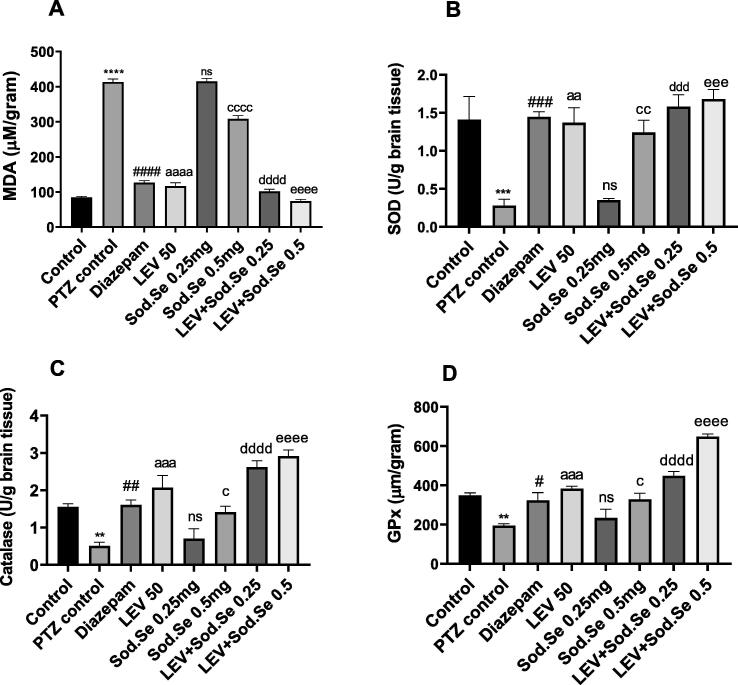
Fig. 11.
Neurochemical analysis of isolated brain depicting the impact of LEV and Sod.Se 0.25 and 0.5 as mono and polytherapy on levels of (A) malondialdehyde, (B) superoxide dismutase, (C) catalase, (D) glutathione peroxidase. The statistical analysis was performed by using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test and data were represented as mean ± S.E.M. (n = 3). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 and ****P < 0.0001 comparison between control and PTZ control, #P < 0.05 , ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001, and ####P < 0.0001 comparison between diazepam and PTZ control, aaP < 0.01, aaaP < 0.001, aaaaP < 0.0001 comparison between LEV and PTZ control, cP < 0.05, ccP < 0.01, ccccP < 0.0001 comparison between Sod.Se 0.5 and PTZ control, dddP < 0.001 and ddddP < 0.0001 comparison between LEV + Sod.Se 0.25 and PTZ control, eeeP < 0.01 and eeeeP < 0.0001 comparison between LEV + Sod.Se 0.5 and PTZ control.