Fig. 2.
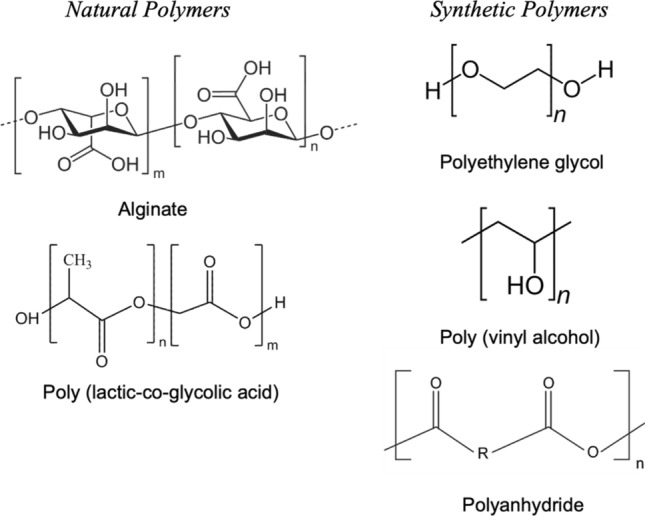
Chemical structure of natural and synthetic polymers used in cell encapsulation. With respect to natural polymers, their advantages include: bioactivity and biocompatibility; however, the key disadvantages include weak mechanical strength, immunogenicity, and uncontrolled rate of degradation. Synthetic polymers on the other hand, are easy to synthesis, have established structures, non-degradable, and possess tunable properties. Conversely, they lack cell adhesion sites
