Figure 3.
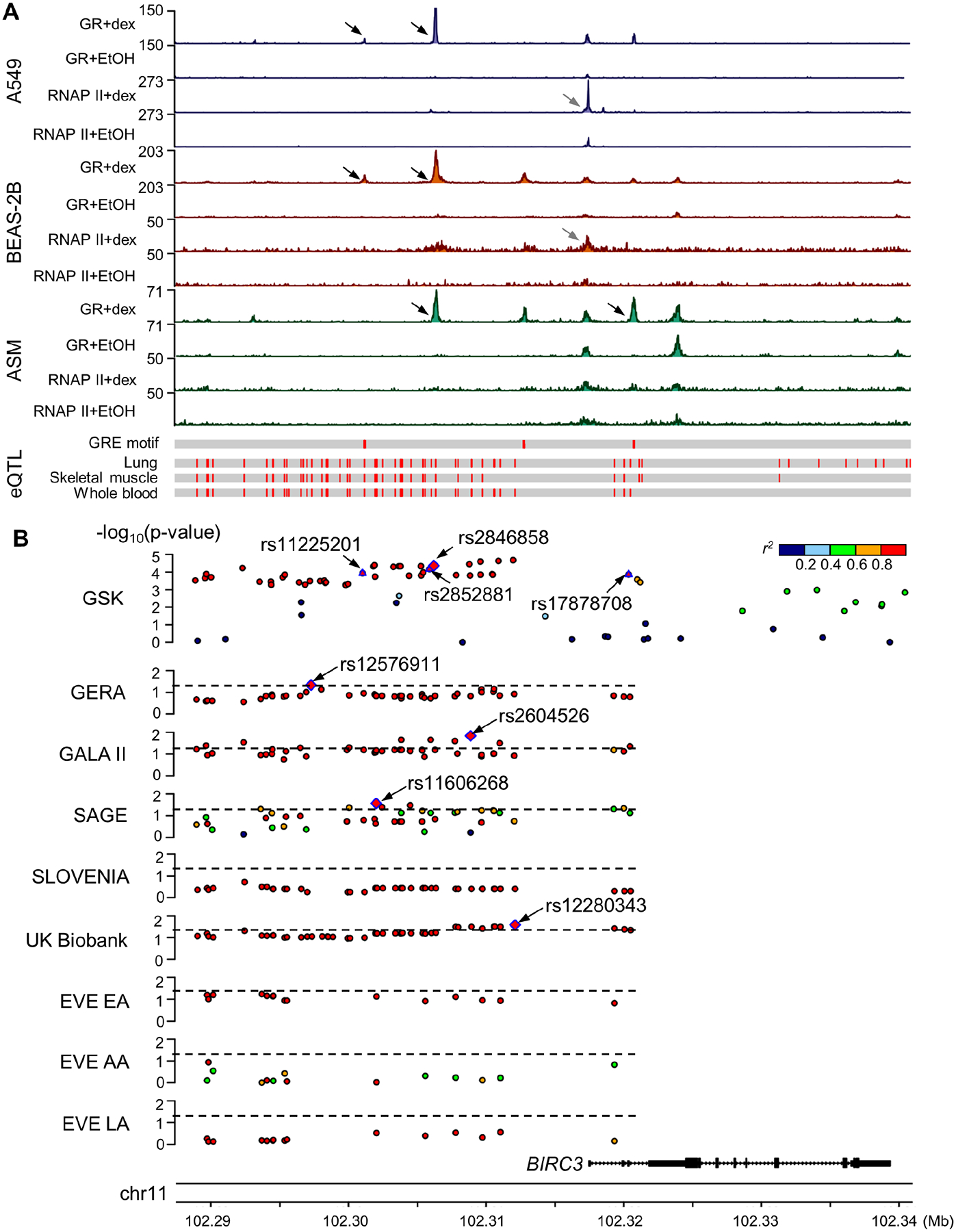
Multiomics evidence supporting BIRC3 as a glucocorticoid response-associated gene. A) ChIP-Seq (top), eQTL (bottom) and B) genetic association results in studies of ICS response and asthma susceptibility near the BIRC3 gene. Black arrows in ChIP-Seq genomic tracks indicate differential binding sites for GR where BIRC3 variants were located and grey arrows indicate differential binding sites for RNAP II. Pairwise r2 was computed between rs2846858 and corresponding variants based on 1000G genotype data that matched the subjects’ race/ethnicity in each study. Four GR-binding site-overlapping SNPs in the GSK study and the top SNPs with p-value<0.05 in replication studies are annotated. Dashed lines indicate p-value of 0.05. AA: African Americans/African Caribbeans; ASM: airway smooth muscle; Dex: dexamethasone; EA: European Americans; EtOH: ethanol; GR: glucocorticoid receptor; GRE: glucocorticoid response element; LA: Latino Americans; RNAP II: RNA polymerase II.
