Figure 1: VMH neuronal activity is dynamically regulated by energy status and BDNF signaling.
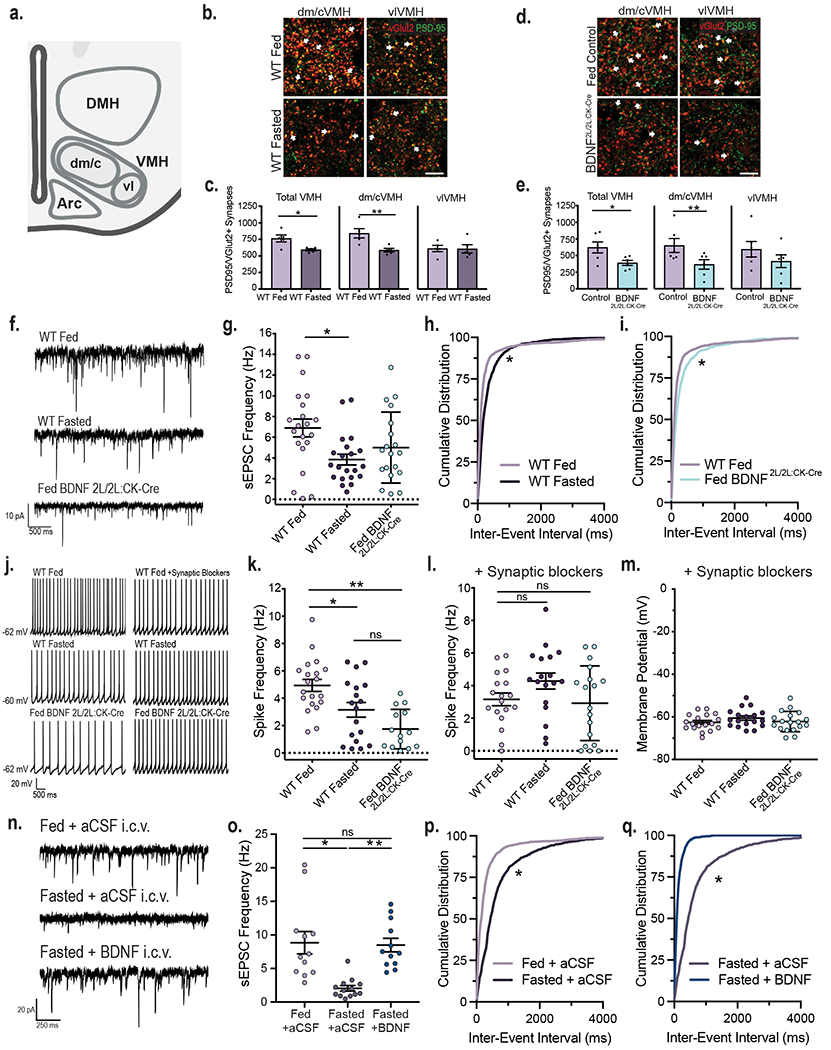
a, Diagram indicating the central/dorsomedial (dm/c) and ventrolateral (vl) regions of the VMH where excitatory synapse density was measured. Created with Biorender.com b, Representative images of VMH tissue from fed and fasted wild type (WT) mice co-immunolabeled with anti-vGlut2 and anti-PSD95. Arrows indicate PSD95 and vGlut2 co-localization (scale bar = 15 uM). c, Quantification of number of excitatory synapses in the VMH of fed and fasted WT mice (n = 5 mice). Student’s unpaired two-sided t-test, *, p = 0.01; **; p = 0.009. d, Representative images of VMH from fed control and BDNF2L/2L:CK-cre mice (scale bar 15 uM). e, Quantification of number of excitatory synapses in the VMH of fed control and BDNF2L/2L:CK-Cre mice (n = 6 mice). Student’s unpaired two-sided t-test, *, p = 0.02; **, p = 0.04. f, Representative traces of sEPSCs in VMH neurons. g, Frequency of sEPSCs in VMH neurons of fed (n = 21 cells) and fasted WT (n = 21 cells) and fed BDNF2L/2LCK:Cre mice (n = 19 cells) from 4 - 6 mice. Ordinary One-way ANOVA, p = 0.01. Tukey multiple comparisons, *, p = 0.01. h, Cumulative distributions of inter-event interval generated from 50 random events per recorded cell for fed and fasted WT (*, p < 0.001, KS = 0.227, Kolmogorov-Smirnov) and i, fed WT and BDNF2L/2LCK:Cre mice (*, p < 0.001, KS = 0.167, Kolmogorov-Smirnov, two-sided). j, Representative traces in current clamp showing VMH neuronal firing. k, Spike frequency of VMH neurons of fed (n = 20 cells) and fasted WT (n = 18 cells) and fed BDNF2L/2LCK:Cre mice (n = 14 cells) (4 – 6 mice per group). Ordinary One-way ANOVA, p < 0.0001. Tukey multiple comparisons, *, p = 0.019; **, p < 0.0001. l, Spike frequency and m, Membrane potential of VMH neurons of fed and fasted WT and fed BDNF2L/2LCK:Cre mice in the presence of 10 uM SR 95531, 50 uM NBQX and 10 uM CPP (n = 18 cells, 3 - 4 mice). Spike Frequency Ordinary One-way ANOVA, p = 0.1078. n, Representative traces of sEPSCs in VMH neurons in Fed WT + aCSF, Fasted WT + aCSF and Fasted WT + BDNF mice. o, Frequency of sEPSCs in VMH neurons in Fed WT + aCSF (n = 12 cells), Fasted WT + aCSF (n = 13 cells) and Fasted WT + BDNF (n = 12 cells) mice (4 mice per group). Ordinary One-way ANOVA, p = 0.0001. Tukey multiple comparisons, *, p < 0.0004; **, p = 0.0007. p, Cumulative distributions of inter-event interval generated from 50 random events per recorded cell for Fed WT + aCSF and Fasted WT + aCSF conditions (*, p < 0.0001, KS = 0.409, Kolmogorov-Smirnov, two-sided) and q, Fasted WT + aCSF and Fasted WT + BDNF conditions (*, p < 0.0001, KS = 0.591, Kolmogorov-Smirnov, two-sided). Data represented as mean +/− SEM.
