Figure 2.
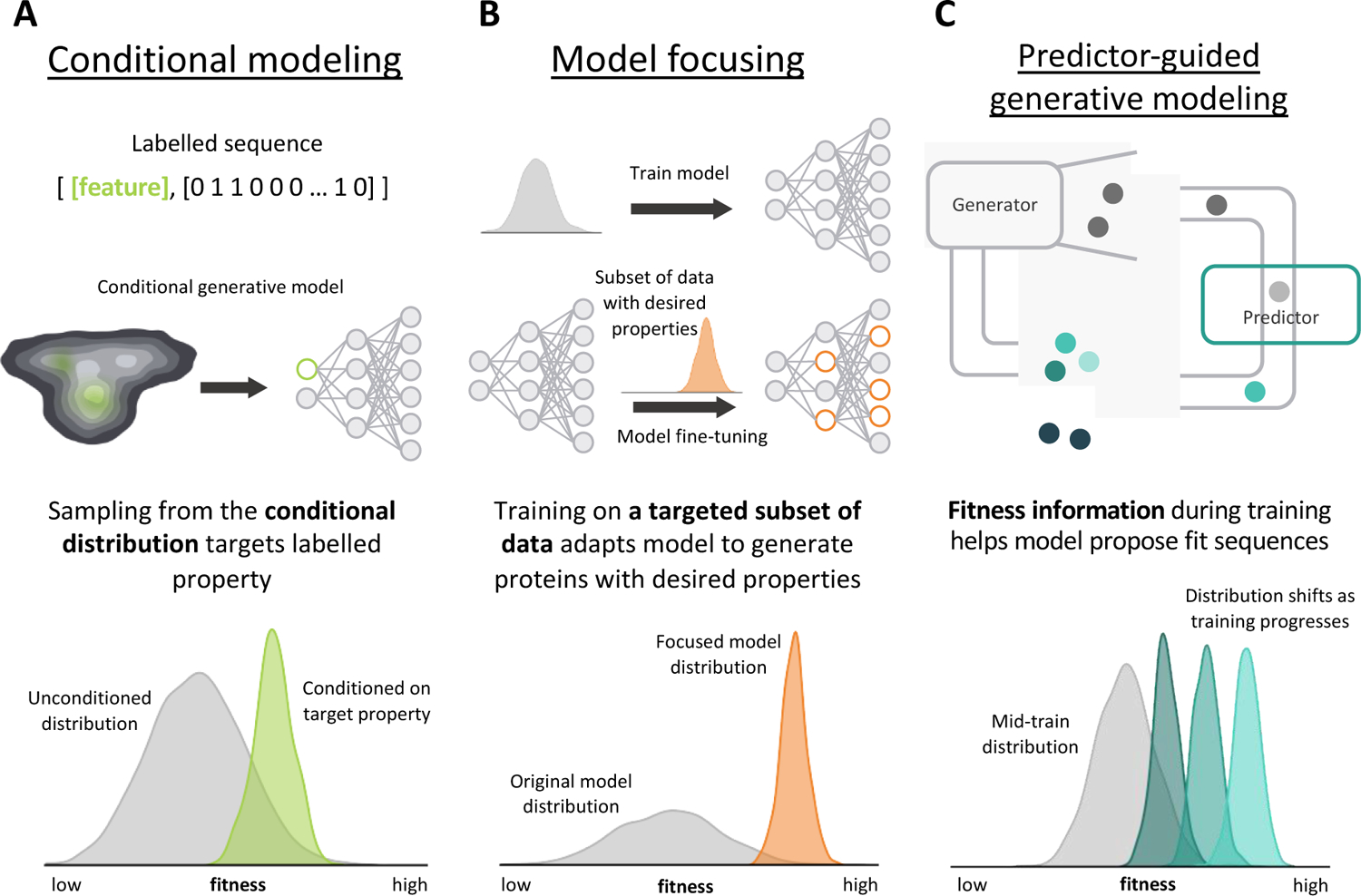
Strategies for protein engineering with generative models. A) Conditional modeling labels training examples with a feature vector to identify sequences with a target attribute. Conditioning on a specific attribute generates a posterior distribution that preferentially samples proteins with the target attribute. B) Model focusing adapts a general model to a specialized task with additional training on a targeted subset of data. Model focusing biases the model to generate proteins with properties that resemble the targeted training set. C) Predictor-guided generative modeling incorporates fitness information into generator training, which can be provided by any model that predicts a property. As generator training progresses, the model proposes more highly fit examples.
