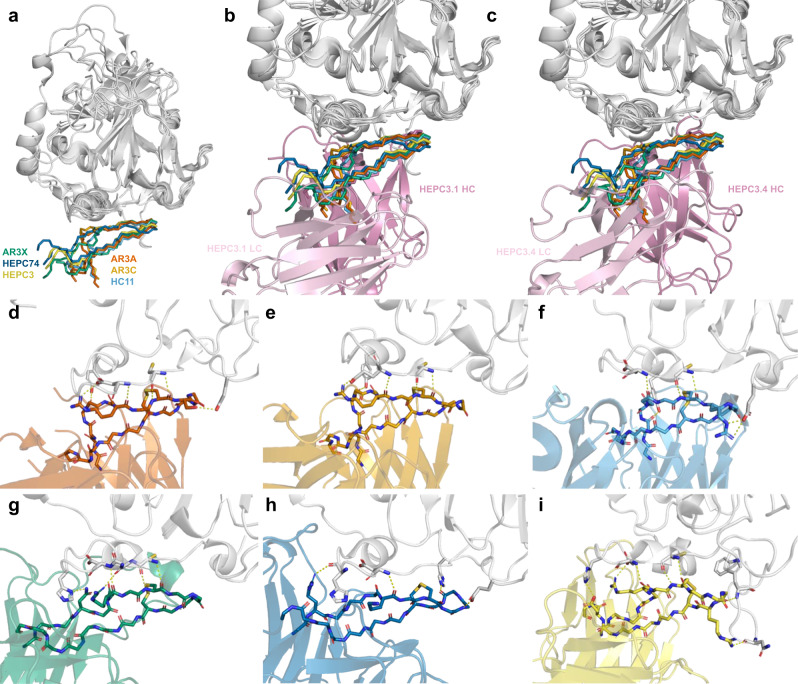
Fig. 4. Interactions of the HCV neutralizing VH1-69 gene-encoded Abs encompassing a common HCDR3 disulfide bond motif with the front layer of HCV glycoprotein E2.
a All six Abs of the described family demonstrate the same pattern of antigen recognition mediated by their HCDR3 loop. Shown is the overlay of the HCV glycoproteins E2 from the co-crystal structures with bNAbs HEPC3, HEPC74, AR3A, AR3C, AR3X, and HC11. The glycoproteins are shown as a gray cartoon. The backbones of the HCDR3 loops of the Abs are shown as sticks. b, c The HCDR3 loop tips of the unliganded HEPC3.1 (b) and HEPC3.4 (c) Fabs were aligned with the observed common antigen recognition pattern of the VH1-69 gene-encoded Abs with an HCDR3 disulfide bond motif. The absence of major clashes suggests that HEPC3.1 and HEPC3.4 Abs might interact with the antigen in the same way as other front layer-specific bNAbs. d–i Polar interactions between HCV glycoprotein E2 and HCDR3 loops of d AR3A, e AR3C, f HC11, g AR3X, h HEPC74, and i HEPC3 Abs, as seen in the crystal structures.