Figure 1. CCR5 KO recipients produce a robust humoral alloimmune response following kidney transplant.
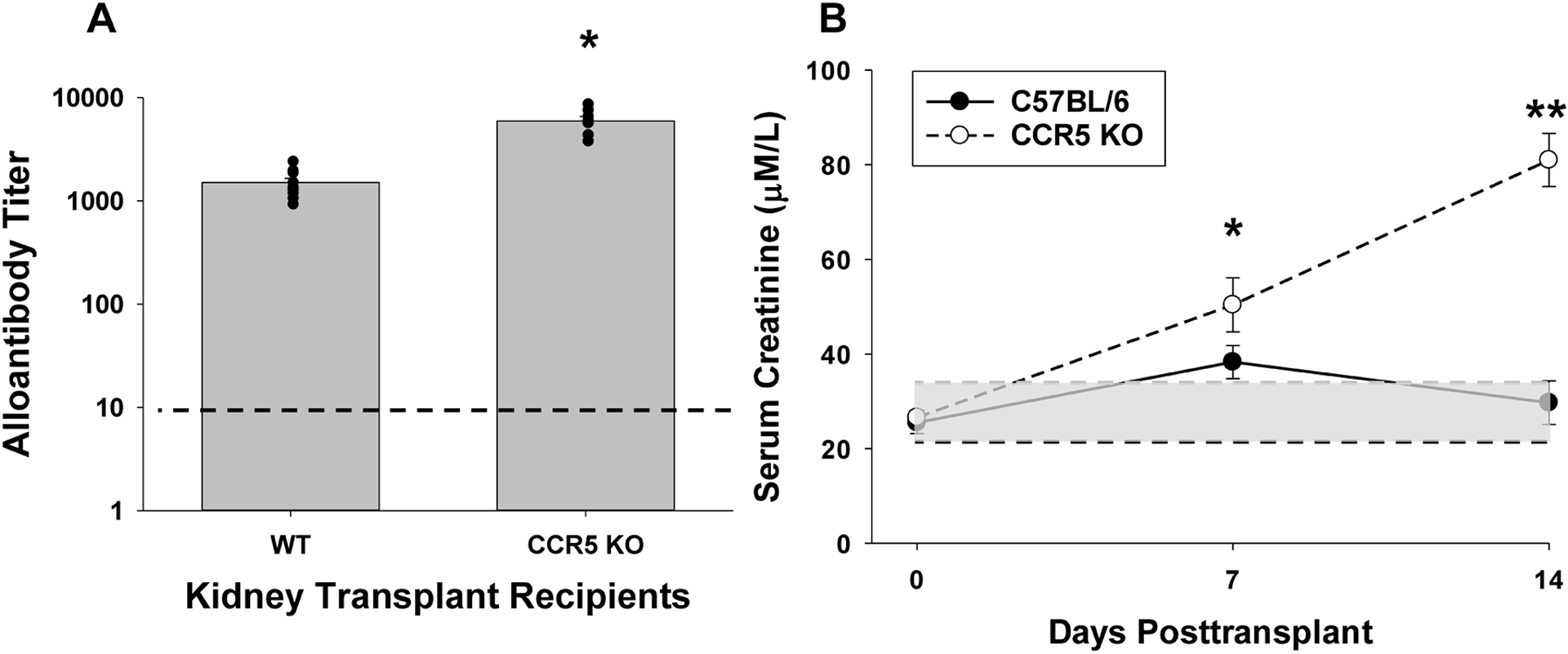
C57BL/6 (wild-type, WT; n=10) and CCR5 KO (n=7) mice (both H-2b) were transplanted with allogeneic (A/J; H-2a) kidneys. A) On day 14, serum was harvested and analyzed for alloantibody titer. CCR5 KO recipients produce significantly more alloantibody compared to WT recipients (6,000±630 vs. 1,500±150, respectively; *p<0.0001). Dashed line represents naïve control sera. B) Kidney allograft survival was assessed in a cohort of WT (n=6) and CCR5 KO (n=5) recipients that underwent concurrent bilateral nephrectomy. Recipient mice were evaluated for serum creatinine (SCr) before and serially following transplant. Posttransplant SCr progressively increased and was significantly higher in CCR5 KO recipients (day 7: 50.4±5.7 μM/L and day 14: 81.0±5.6 μM/L) compared to WT recipients (day 7: 38.3±3.5 μM/L, *p=0.047; day 14: 29.7±4.6 μM/L, **p<0.0001). No difference in SCr was observed prior to transplant between CCR5 KO and WT mice (WT: 25.5±2.4 μM/L, CCR5 KO: 26.6±1.4 μM/L, p=ns). Gray shaded area indicates normal range of SCr for C57BL/6 recipients (21–35 μM/L). Dark dotted line indicates mean serum creatinine in naïve C57BL/6 mice.
